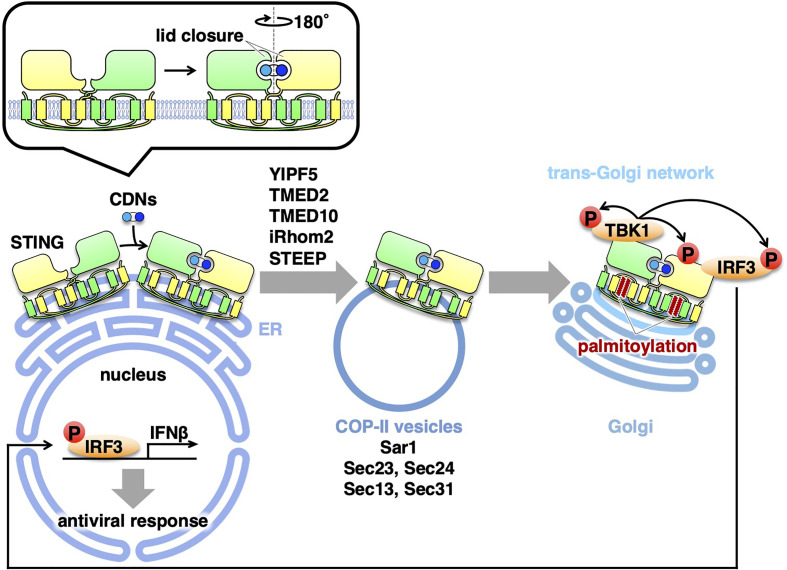
Figure 1.
Exocytic membrane traffic of STING from the ER. STING localizes at the ER at the steady-state. Upon binding to CDNs, STING translocates from the ER to the Golgi with COP-II vesicles. Several proteins (YIPF5, TMED2, TMED10, iRhom2, and STEEP) associated with the COP-II components are required for the translocation of STING. After reaching the Golgi, STING undergoes palmitoylation and activate TBK1 at the trans-Golgi network.