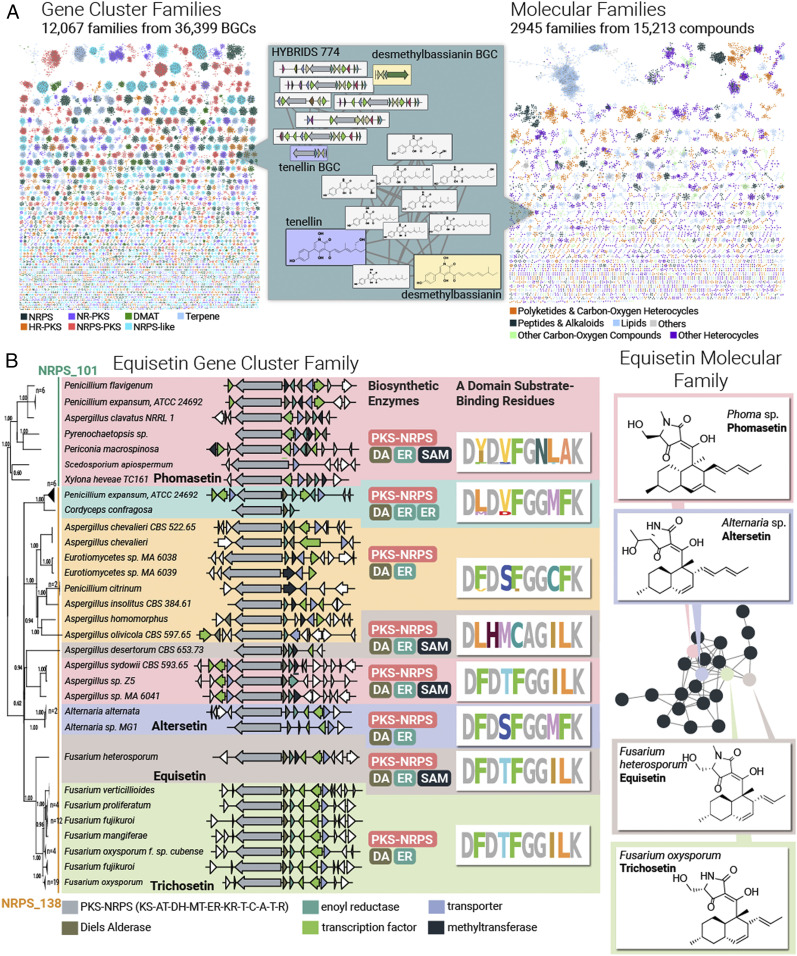
Fig. 3.
Large-scale analysis of fungal genome-encoded and known metabolite scaffolds. (A) Colliding large-scale collections of fungal genetic content (Left) and fungal natural products (Right) using a network of GCFs interpreted from 1,037 genomes (Left) and 15,213 metabolites arranged into 2,945 molecular families based on their Tanimoto similarity score (Right). Note that 92% of these 12,067 GCFs remain unassigned to their metabolite products. (B) Variations in adenylation domain substrate-binding residues and tailoring enzyme composition facilitate modifications to the equisetin GCF (Left) and MF (Right). The phylogram to the left represents a maximum likelihood tree based on the hybrid NRPS–PKS backbone enzyme. All branches in this tree have >50% bootstrap support.