FIGURE 2.
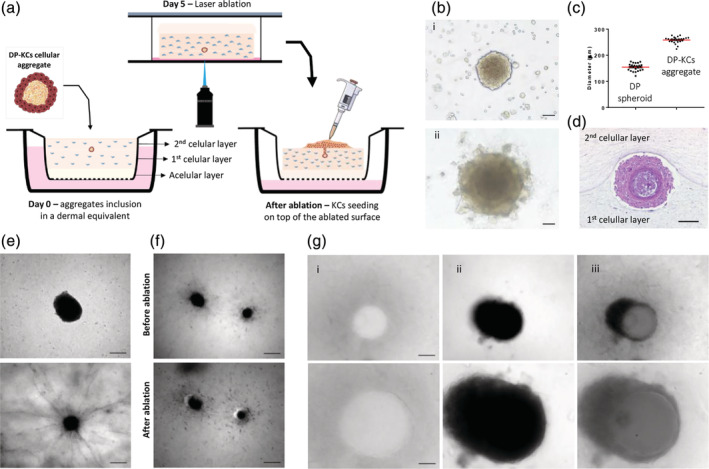
Ablation of 3D microchannels in the fibroblast‐laden hydrogels. (a) Schematic representation of the procedure adopted to incorporate DP cells‐KCs aggregates between fibroblast‐embedded collagen layers, the ablation of a microchannel connecting the hydrogel surface to the aggregate and the subsequent seeding of KCs on top of the ablated surface. (b) Phase‐contrast image of DP spheroids co‐cultured with a suspension of KCs (i) and the DP cells‐KCs aggregates formed after 2 days of culture (ii). (c) Quantification of the diameter of DP cells‐KCs aggregates and DP spheroids. (d) Representative H&E image of a DP cells‐KCs cellular aggregate 5 days after its incorporation in the dermal‐like collagen layer. (e) Representative light microscopy images of a DP cells‐KCs aggregate (top) and a DP spheroid (bottom) inside the collagen matrices after 5 days in culture, respectively showing maintenance of the structure and the outgrowth of the DP cells into the collagen. (f) Light microscopy images of DP spheroids before and after the creation of an off‐centered microchannel by MGLA. (g) Light microscopy images of the microchannel at the top of the hydrogel (i) and just before the DP cells‐KCs aggregate (ii), and the corresponding overlap (iii), denoting the position of the ablated microchannels in relation to the DP cells‐KCs aggregate. Bottom images are higher magnifications of the top ones. Scale bars are 200 μm for (e—top image, f), 100 μm for (d, g—top image) and 50 μm for (b, e, and g—bottom images)
