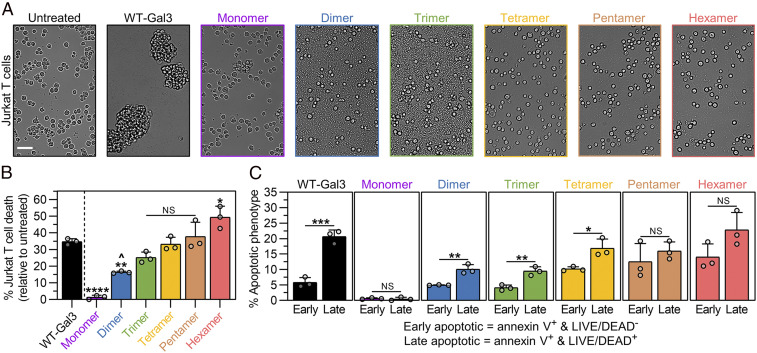
Fig. 3.
Cell agglutination and death signaling activities of synthetic Gal3 constructs. (A) Brightfield microscopic images taken of Jurkat T cells after 18 h incubation with synthetic Gal3 constructs, wild-type Gal3 (WT-Gal3), or PBS (untreated control). (Scale bar, 50 µm.) (B) Percentage of Jurkat T cell death after 18 h treatment with synthetic Gal3 constructs or WT-Gal3, shown relative to the untreated control. (C) Percentage of Jurkat T cells in the early apoptotic and late apoptotic populations after 18 h treatment with synthetic Gal3 constructs or WT-Gal3, shown relative to the untreated control. For B, n = 3, mean ± SD, */^P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001, NS is no significant difference, and comparisons were made using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc. Statistical comparisons relative to WT-Gal3 are denoted by * or NS symbol. Statistical comparison relative to Monomer is denoted by ^ symbol. For C, n = 3, mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, NS is no significant difference, and comparisons were made using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test. All experiments were performed at an equimolar concentration of sfGFP or Gal3 = 5 µM (i.e., [WT-Gal3] = 5 µM, [Monomer] = 5 µM, [Dimer] = 2.5 µM, [Trimer] = 1.67 µM, [Tetramer] = 1.25 µM, [Pentamer] = 1 µM, [Hexamer] = 0.83 µM).