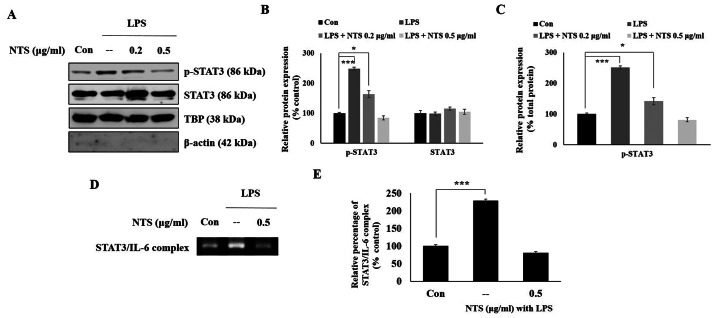
Figure 4.
NTS inhibits the expression levels of nuclear p-STAT3 and its binding to the IL-6 promoter. (A) Western blotting of the nuclear extracts of C2C12 cells showing the expression of STAT3 and p-STAT3 nuclear proteins following treatment with 100 ng/ml LPS and 0.2 or 0.5 µg/ml NTS for 24 h. (B) Relative expression levels of STAT3 and p-STAT3 nuclear proteins were determined via densitometry and normalized to TBP. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (C) Relative expression levels of nuclear p-STAT3 determined via densitometry and were normalized to total STAT3. (D) ChIP analysis of STAT3-IL-6 complex formation in C2C12 cells following treatment with 100 ng/ml LPS or 0.5 µg/ml NTS for 24 h. Data were quantified using reverse transcription-semi-quantitative PCR. (E) Relative STAT3-IL-6 complex binding obtained in C2C12 cells with 100 ng/ml LPS or 0.5 µg/ml NTS for 24 h by ChIP assay and expressed as a percentage of the control. Data are representative of three independent experiments. *P<0.05 and ***P<0.001 vs. control. NTS, non-toxic sulfur; p-, phosphorylated; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; Con, control; TBP, Tata-binding protein.