Figure 4. CerS6/C14-ceramide and SphK2/S1P crosstalk induces aging-dependent mitophagy in activated T cells.
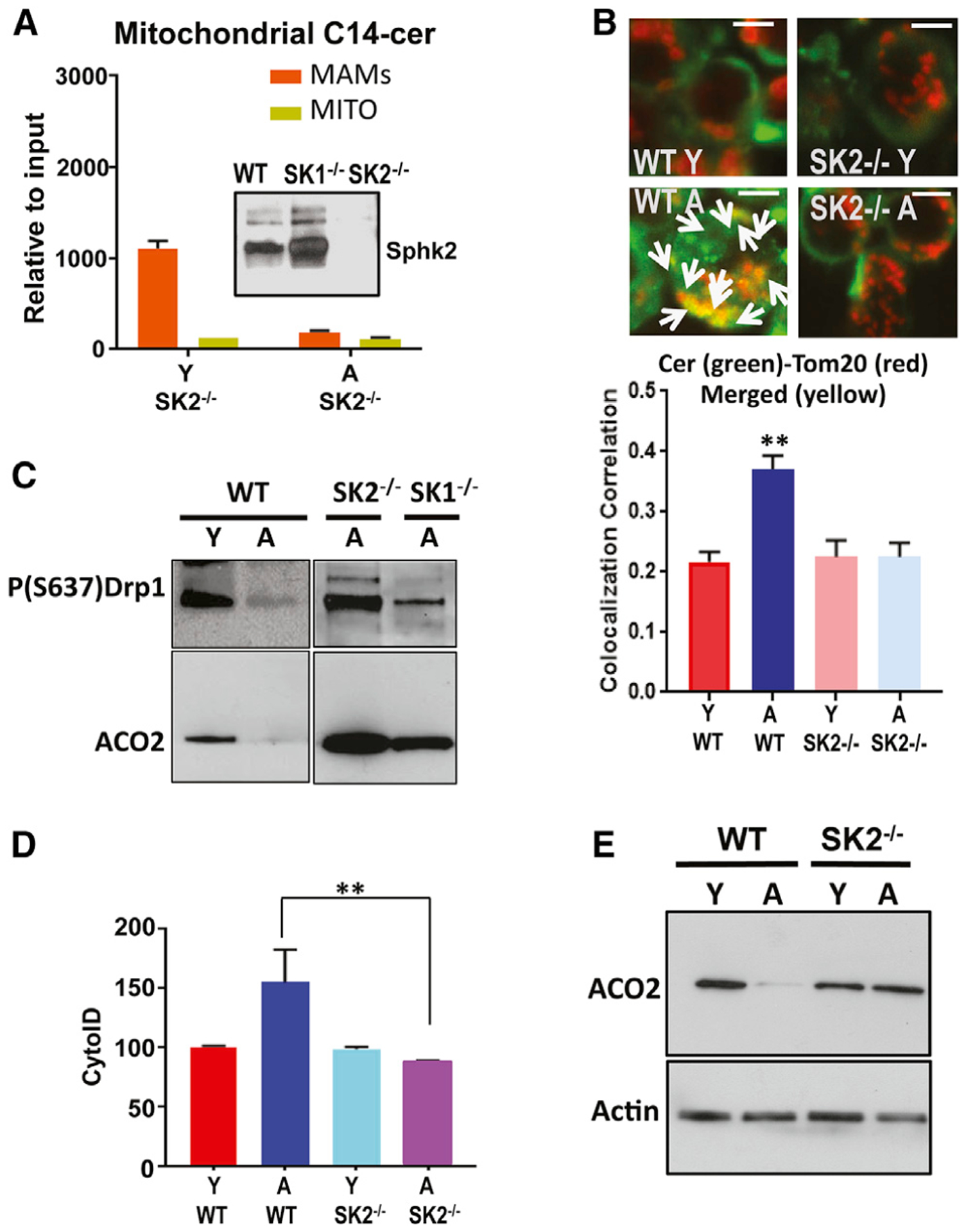
(A) Mitochondrial accumulation of C14 ceramide was measured using mass spectrometry/lipidomics in activated T cells obtained from Y and A SphK2−/− (SK2) mice in MAMs and MITO-enriched fractions.
(B) Colocalization of ceramide (green) and TOM20 (red) was measured to detect mitophagy in activated T cells isolated from Y and A WT and SphK2−/− (SK2) mice. Lower panel indicates the quantification of colocalization (Rc). Data are means ± SDs from 3 independent experiments (n = 3). **p < 0.01 as determined by Student’s t test.
(C) P(S637)-Drp1 and ACO2 protein abundance was measured by western blotting in T cells isolated from Y and A WT or A SphK2−/− (SK2) and SphK1−/− (SK1) mice.
(D and E) TCR-activated T cells obtained from Y and A WT or SphK2−/− (SK2) mice were used for the detection of LC3/autophagy by cyto-ID (D) and ACO2 degradation by mitophagy using western blotting (E). Actin was used as a loading control (E). These studies represent 3 independent experiments (n = 3). **p < 0.01 as determined by Student’s t test in (D).
