Fig. 5.
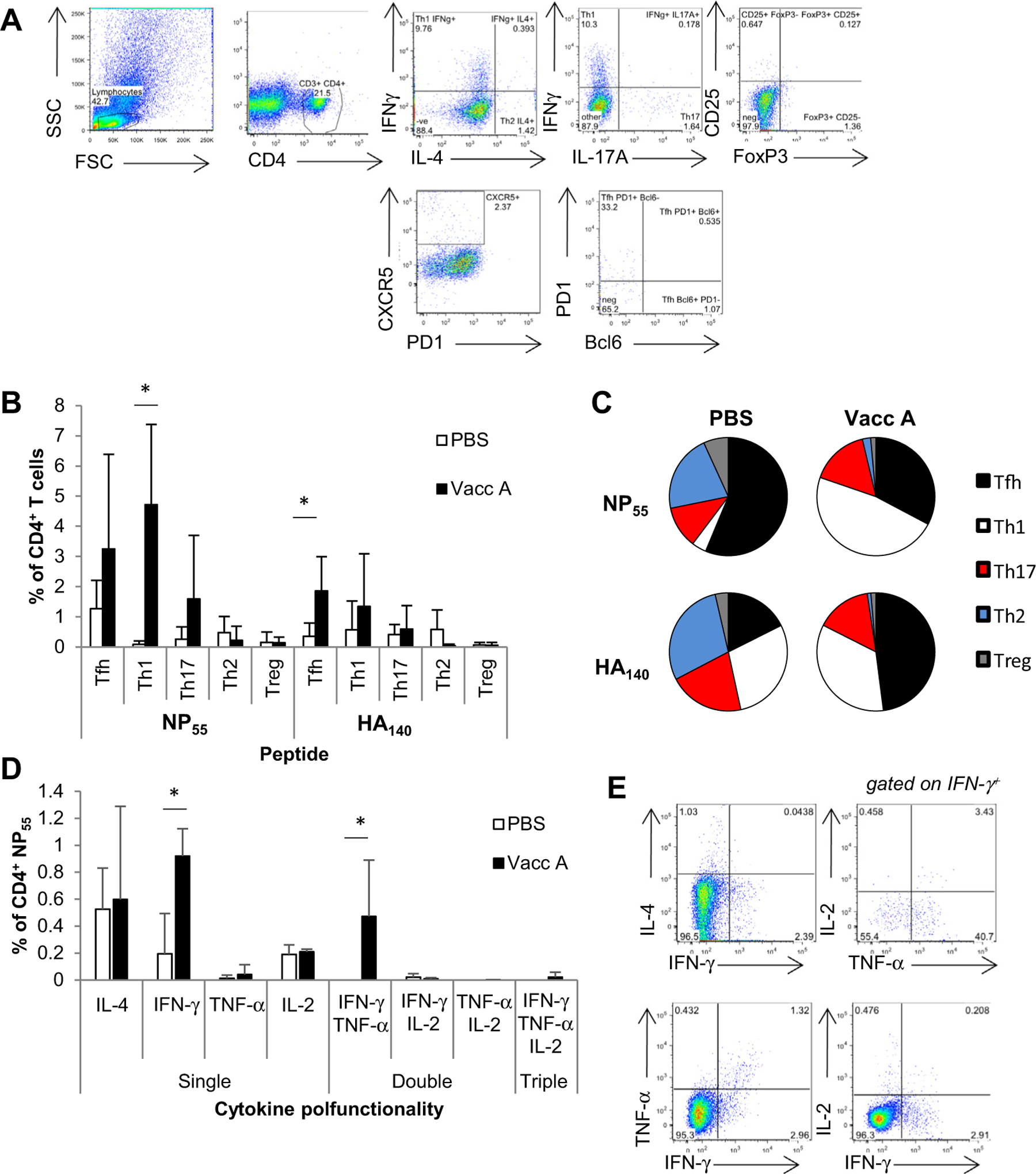
Vaccination increases Tfh and Th1 CD4+ T cell phenotype responses. BALB/c mice were vaccinated twice or received PBS, infected with H3N2 1LD50, and day 7 post infection BAL harvested. Cells were stained with a panel of antibodies representing CD4+ T cell phenotype profiles (A), stimulated with MHC-II restricted peptides, NP55 and HA140, for cytokine production of IFN-γ+ and IL-4, and analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) The CD4+ T cell panel was assessed for Tfh (CD4+ CXCR5+), Th1 (CD4+ IFN-γ+), Th2 (CD4+ IL-4+), Th17 (CD4+ IL-17A+) d and Treg (CD4+ CD25+ FoxP3+). Tfh cells were also assessed for PD1 and Bcl6 expression, and Th17 cells for RORγt which was low in the BAL, and not included in the analysis. (B) The cytokine specific and phenotype response was determined for NP55 and HA140 peptides (data represents n = 3, mean+/−stdev), and (C) their proportions. (D) Polyfunctional cytokine production was also assessed for NP55 responses in the BAL from day 7 H3N2 infection, for Th1 (IFN-γ, TNF-α and IL-2) and Th2 (IL-4) cytokines (data represents n = 3, mean+/−stdev). (E) CD4+ T cells gated for single, double and triple cytokine production. Experiment repeated at least twice, *p > 0.01 vs PBS controls (by t-test).
