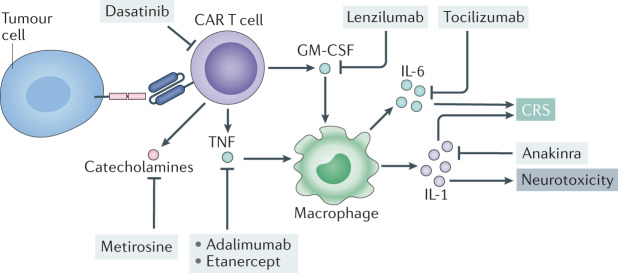
Fig. 3. Schematic representation of current and potential therapeutic interventions for CRS.
Blockade of the IL-6 receptor (IL-6R; using the monoclonal antibody tocilizumab) has shown clinical benefit in patients with cytokine release syndrome (CRS)4,6,29,33. In vivo and in vitro models have proposed novel therapeutic interventions for CRS that directly target pro-inflammatory cytokines — such as IL-1 (the IL-1 receptor antagonist anakinra)29,33,110,116, tumour necrosis factor (TNF; adalimumab or etanercept)52 and granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF; lenzilumab)48,50 — or other pro-inflammatory mediators such as catecholamines (for example metirosine, which inhibits catecholamine synthesis)60. Furthermore, kinase inhibitors such as dasatinib can inhibit chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell functionality, with subsequent reduction in effector cytokine secretion108. Other broad-spectrum small-molecule inhibitors, such as ruxolitinib and ibrutinib (not shown here), that can broadly inhibit cytokine signalling and cytokine production across multiple cell types have been proposed for use in CRS.