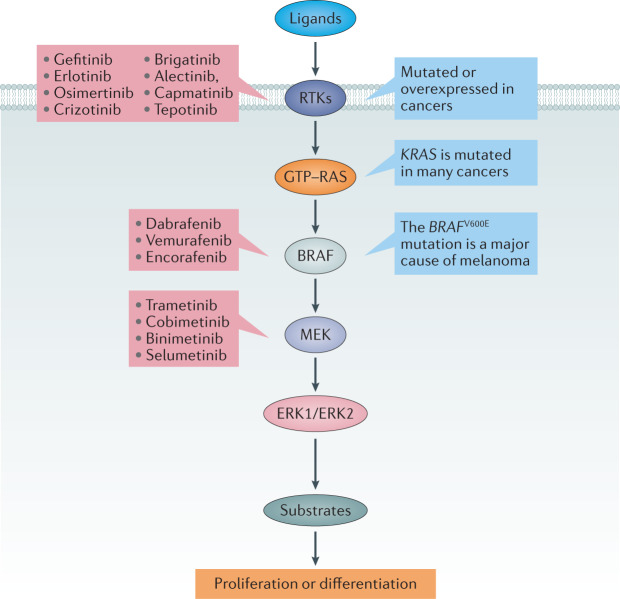
Fig. 2. Mutations in the classical MAP kinase cascade cause cancer.
The classical mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade is frequently hyperactivated in lung and other cancers owing to the overexpression or mutation of receptor tyrosine kinases, such as the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), ALK and MET, and more downstream effectors that are most commonly RAS and BRAF. Examples of drugs that target the EGFR (gefitinib, erlotinib and osimertinib), ALK (crizotinib, brigatinib and alectinib) and MET (capmatinib and tepotinib) are highlighted in red. The three approved inhibitors of BRAF and the four approved inhibitors of MEK1 and MEK2 are also shown.