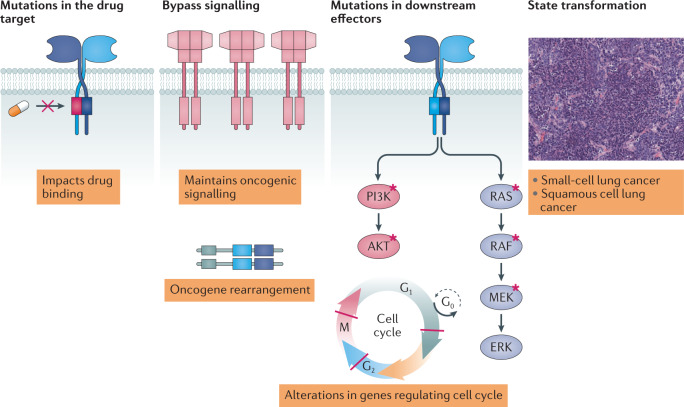
Fig. 3. Mechanisms that can cause drug resistance.
Drug resistance occurs primarily through four main mechanisms. Acquired drug resistance mutations most commonly affect the binding of the drug to its target. Acquired oncogenic amplifications or rearrangements can activate downstream signalling to bypass inhibition of the drug target. Mutations in downstream effectors can activate signalling pathways despite effective inhibition of an upstream kinase target. State transformation can lead to kinase inhibitor insensitivity.