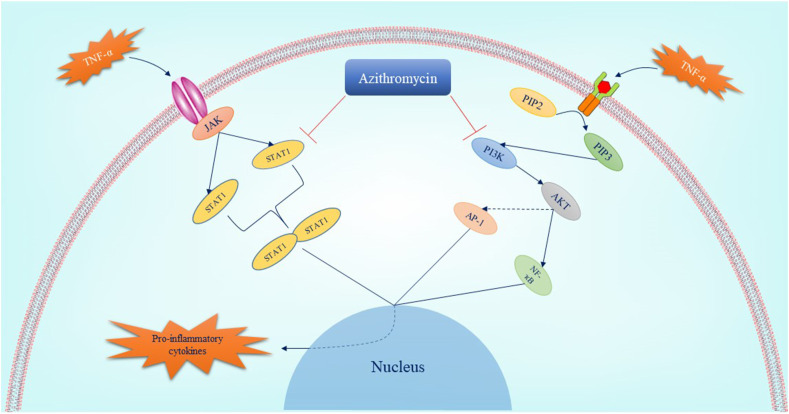
Fig. 1.
The pathways which are inhibited by azithromycin leading to hyper inflammation suppression. Azithromycin suppresses two main pathways involved in pro-inflammatory cytokines production including janus kinase (JAK)/STAT and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. As a result, azithromycin inhibits the activation of AP-1, NF-ҡB, and STAT dimerization by mediating these pathways suppression. Reduction of the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as ILs, TNF-α is the result of this inhibition. AP-1: activated protein-1; IL: interleukin; JAK: Janus kinase; NF-ҡB: Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase; STAT: Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α.