Figure 4: Pathophysiology of huperuricosuric calcium urolithiasis.
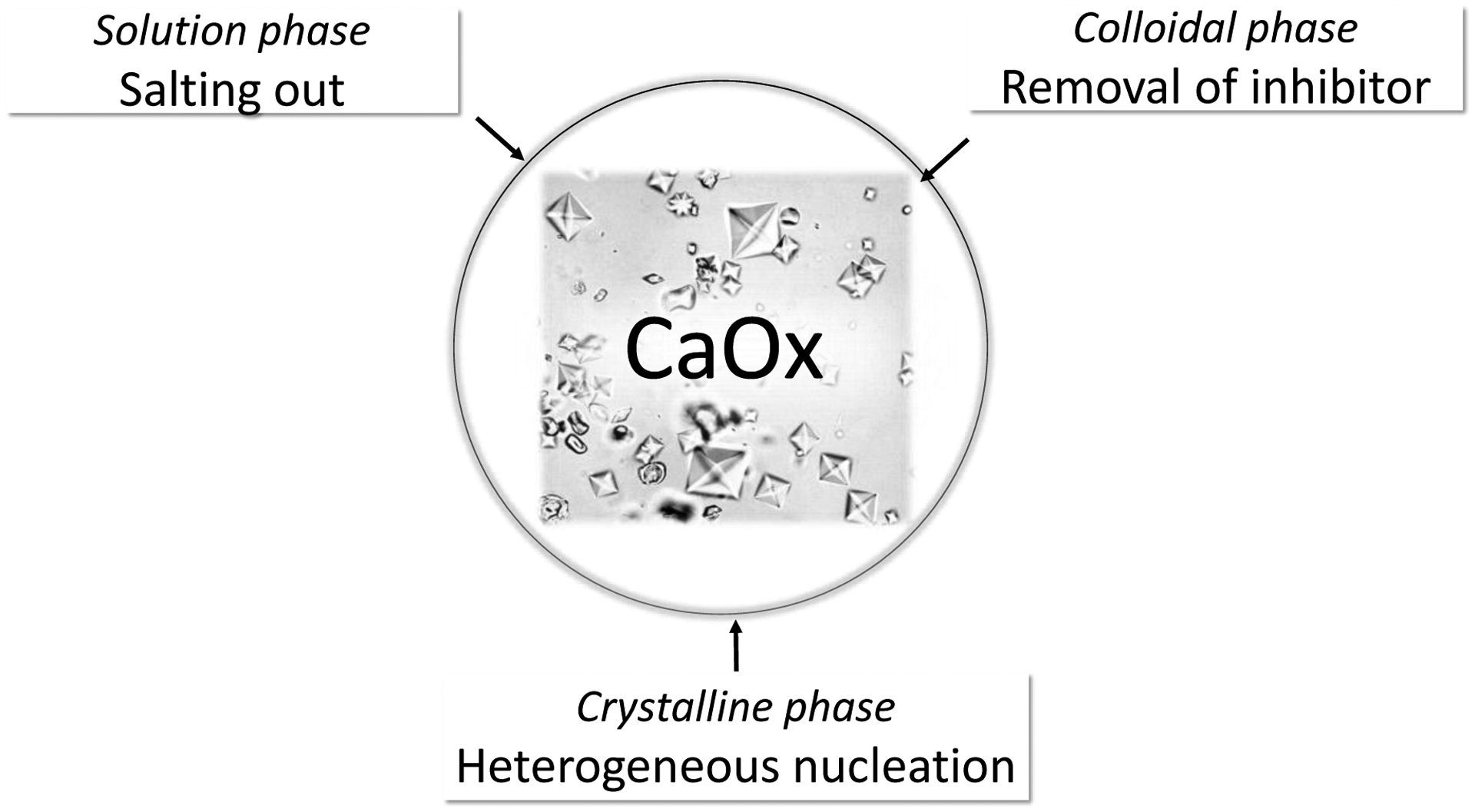
In the solution phase, sodium urate is a potent salting out agent that can increase the activity product of calcium oxalate. In the colloidal phase, sodium urate can adsorb and remove inhibitors of calcium oxalate crystallization. Finally, sodium urate crystals can initiate calcium oxalate crystallization via heterogeneous nucleation or epitaxy.
