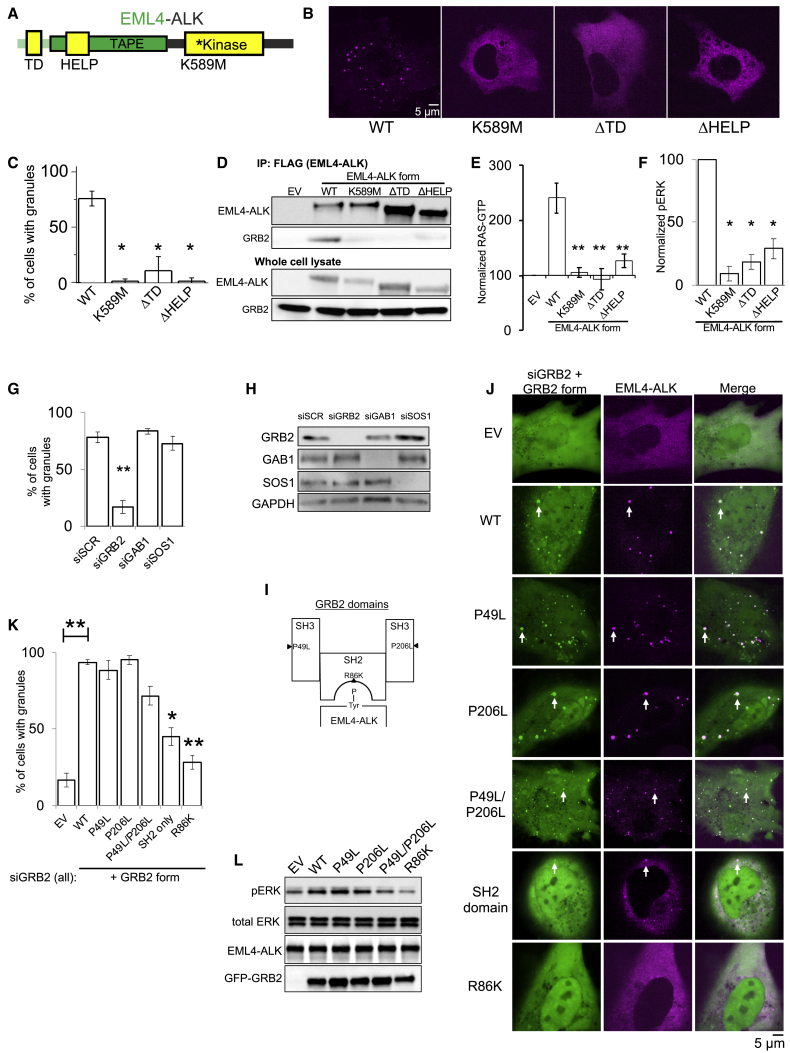
Figure 4.
Protein granule formation by EML4-ALK is critical for RAS/MAPK signaling
(A) Domain structure schematic of EML4-ALK.
(B) Live-cell imaging of mTagBFP2::EML4-ALK wild-type (WT) or mutant forms in Beas2B cells.
(C) Quantification of % cells with granules (6 or greater). 75 cells per condition, n = 3.
(D) Anti-FLAG co-IP of FLAG-tagged WT or mutant EML4-ALK forms in 293T cells, followed by GRB2 western blotting. n = 3.
(E and F) Endogenous RAS-GTP levels (E) and ERK activation (F) by western blotting upon expression of EML4-ALK WT or mutant forms in 293T cells. n = 4. See STAR Methods for normalization details.
(G and H) Live-cell imaging of mTagBFP2::EML4-ALK in Beas2B cells after small interfering RNA (siRNA) treatment (72 h). Quantification of % cells with granules, 100 total cells, n = 3 (G). Representative images in Figure S4D. Western blotting for siRNA knockdown, n = 3 (H).
(I) Structure schematic of adaptor protein GRB2.
(J) Live-cell imaging of mTagBFP2::EML4-ALK and mEGFP-labeled GRB2 mutants in Beas2B cells after 72 h siRNA against endogenous GRB2. SH2 only denotes the GRB2 SH2 domain. Arrows indicate representative EML4-ALK granules with local enrichment of GRB2 mutants (multiple non-highlighted granules also show colocalization).
(K) Quantification of % cells with EML4-ALK granules (6 or greater). 75 total cells per condition, n = 3.
(L) Western blotting upon co-expression of EML4-ALK and mEGFP-labeled GRB2 mutants in 293T cells after 72 h of siRNA against endogenous GRB2.
For all panels, error bars represent ±SEM, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s HSD test.