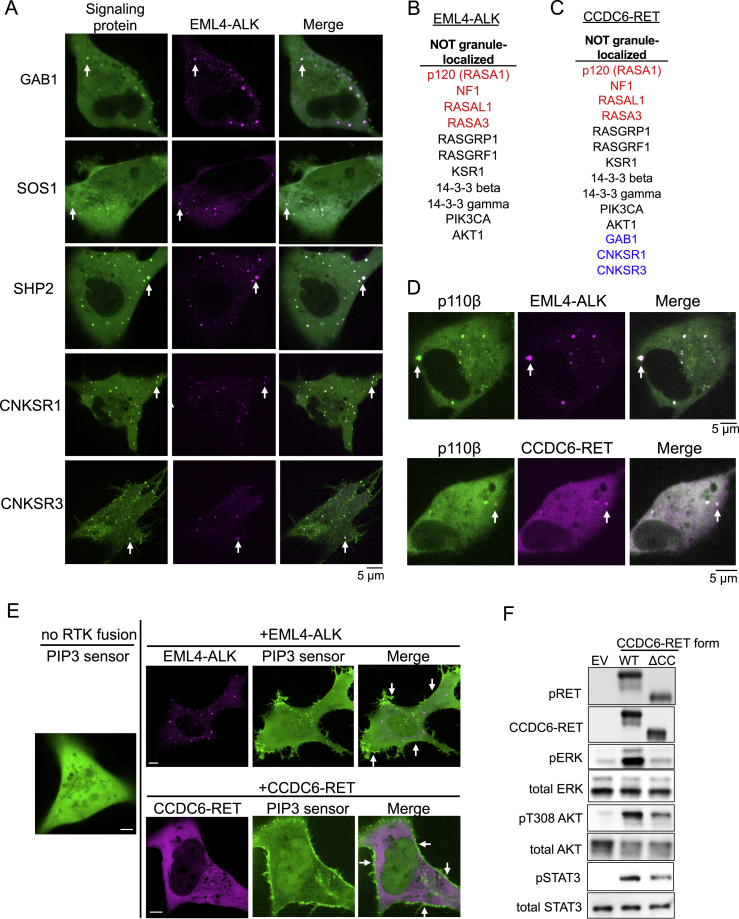
Figure S7.
Signaling components of membraneless RTK protein granules, related to Figure 7
(A) Live-cell confocal imaging of mTagBFP2::EML4-ALK and mEGFP-tagged signaling proteins expressed in Beas2B cells. White arrows indicate a representative EML4-ALK protein granule with local enrichment of respective signaling proteins (multiple non-highlighted granules also show colocalization between EML4-ALK and signaling proteins). Images are representative of at least 20 cells analyzed in 3 independent experiments with greater than 80% colocalization observed for all signaling proteins.
(B, C) List of proteins that were mEGFP-tagged and did not enrich at mTagBFP2::EML4-ALK or mTagBFP2::CCDC6-RET protein granules upon expression in Beas2B cells. RAS GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) are displayed in red, proteins with differential localization between EML4-ALK and CCDC6-RET are displayed in blue.
(D) Live-cell confocal imaging of mEGFP::p110β and mTagBFP2::EML4-ALK or mTagBFP2::CCDC6-RET expressed in Beas2B cells. White arrows indicate a representative RTK protein granule with local enrichment of p110β (multiple non-highlighted granules also show enrichment of p110β).
(E) Live-cell confocal imaging of PI3K activity reporter (mCherry-tagged AKT2-PH domain, which functions as a PIP3 sensor) alone or with mTagBFP2::EML4-ALK or mTagBFP2::CCDC6-RET expression in Beas2B cells. White arrows indicate plasma membrane enrichment of the PI3K activity reporter.
(F) Western blotting upon expression of wild-type CCDC6-RET or non-granule-forming, coiled-coil domain deletion mutant ΔCC in 293T cells. EV denotes empty vector. Images are representative of at least 5 independent experiments.