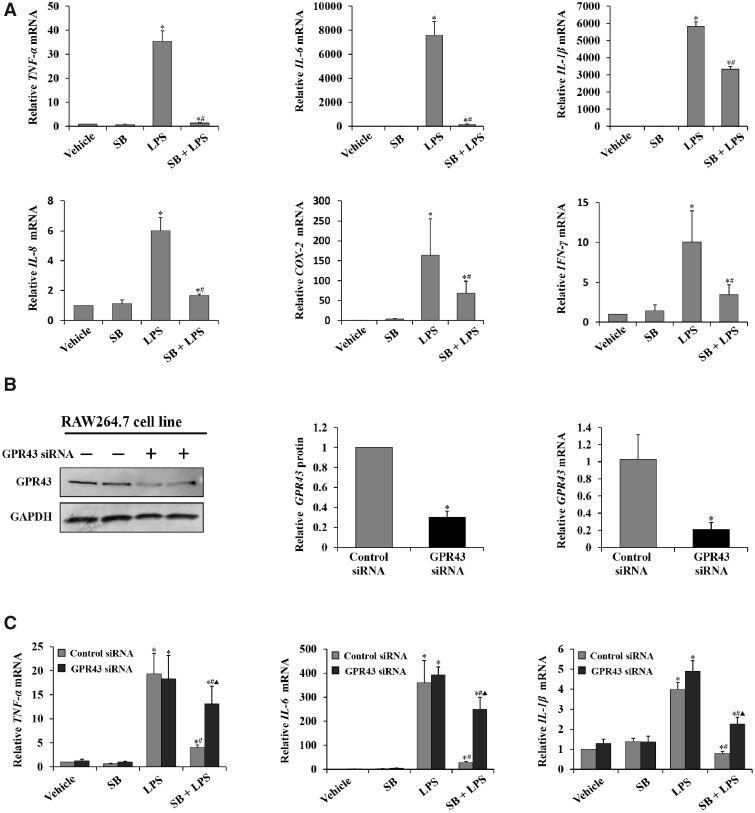
Figure 3.
Sodium butyrate/GPR43 ameliorated liver injury and inflammation via repressing macrophage activation. (A) RT-PCR was used to determine relative mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, IL-8, COX-2, and IFN-γ produced by RAW264.7 cell line. *P < 0.05 vs vehicle group; #P < 0.05 vs LPS group. Values are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6 per group). (B) Expression of GPR43 in RAW264.7 cells was detected by Western blot. Levels of GAPDH are shown as a loading control; relative quantitative evaluation of the Western-blot analysis for the normalized GPR43/GAPDH was analysed from the Western-blot assay (values are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 6 per group, Bonferroni’s comparison post-hoc test). The relative mRNA level of GPR43 expression was detected to evaluate the siRNA interference ratio. (C) RT-PCR was used to determine relative mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β produced by RAW264.7 cell line transfected with GPR43 siRNA RNA oligo (GPR43 siRNA) or control siRNA RNA oligo (Control siRNA). *P < 0.05 vs vehicle group in the same type of cell; #P < 0.05 vs LPS group in the same type of cell; P < 0.05 vs SB + LPS group in control siRNA group. Values are expressed as mean ± SD (n = 6 per group). RT-PCR, real-time polymerase chain reaction; SB, sodium butyrate.