Figure 6.
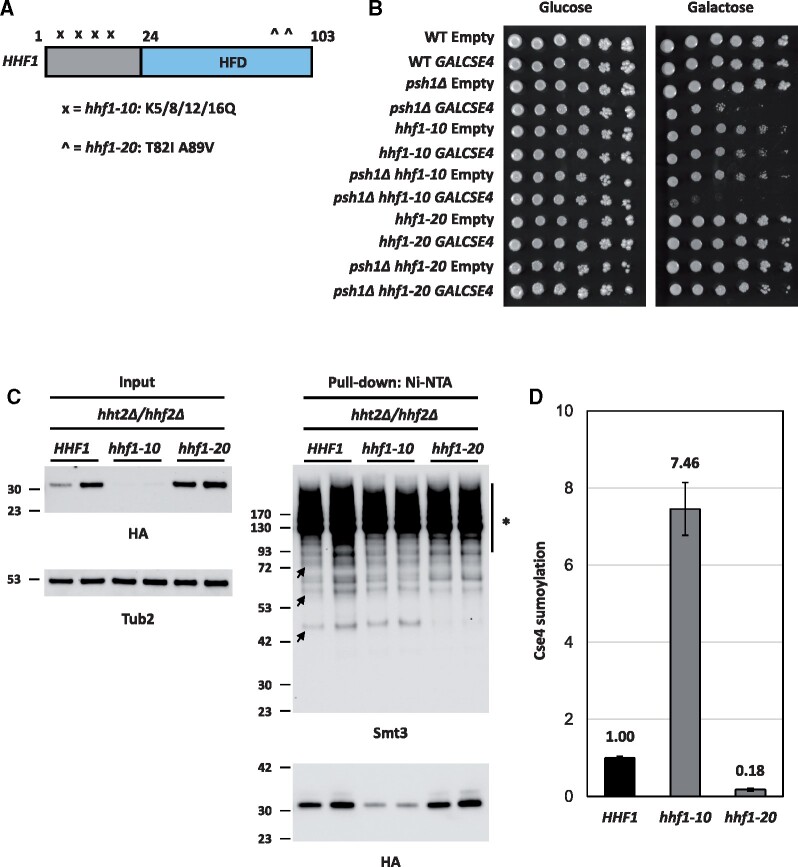
Mutation in the histone fold domain of histone H4 suppresses the SDL phenotype of a psh1Δ GALCSE4 strain and causes defects in Cse4 sumoylation. (A) Schematic of HHF1. Displayed is a cartoon of the HHF1 gene with mutations in hhf1-10 indicated by an “x” and hhf1-20 with a “^” in the histone fold domain (HFD, blue). The specific residues mutated in each allele are indicated below the schematic. (B) Mutations in the histone fold domain of histone H4 suppress the SDL phenotype of a psh1Δ GALCSE4 strain. Growth assays of wild-type (MSY559), psh1Δ (YMB11346), HHT1/hhf1-10 (MSY535), HHT1/hhf1-20 (MSY534), psh1Δ HHT1/hhf1-10 (YMB11347), and psh1Δ HHT1/hhf1-20 (YMB11348) with empty vector (pMB433) or expressing GAL1-6His-3HA-CSE4 (pMB1458). Cells were plated in fivefold serial dilutions on selective media plates containing either glucose (2% final concentration) or raffinose/galactose (2% final concentration each). Plates were incubated at 30°C for three to five days. Three independent transformants were tested and a representative image is shown. (C) Mutations in the histone fold domain of histone H4 decrease levels of sumoylated Cse4. The levels of sumoylated Cse4 were determined using lysates from HHT1/HHF1 (MSY559), HHT1/hhf1-10 (MSY535), and HHT1/hhf1-20 (MSY534) strains in the hht2Δ/hhf2Δ background, transformed with pGAL-8His-HA-CSE4 (pMB1345), as described in Figure 5A. Arrows indicate the three high molecular weight bands that represent sumoylated Cse4. Asterisk indicates nonspecific sumoylated proteins that bind to beads. (D) Quantification of the relative levels of sumoylated Cse4 in hhf1 strains. Levels of sumoylated Cse4 were normalized to nonmodified Cse4 probed against HA in the pull-down samples and levels in the HHT1/HHF1 strain were set to 1. Error bars indicate average deviation from the mean from two biological replicates.