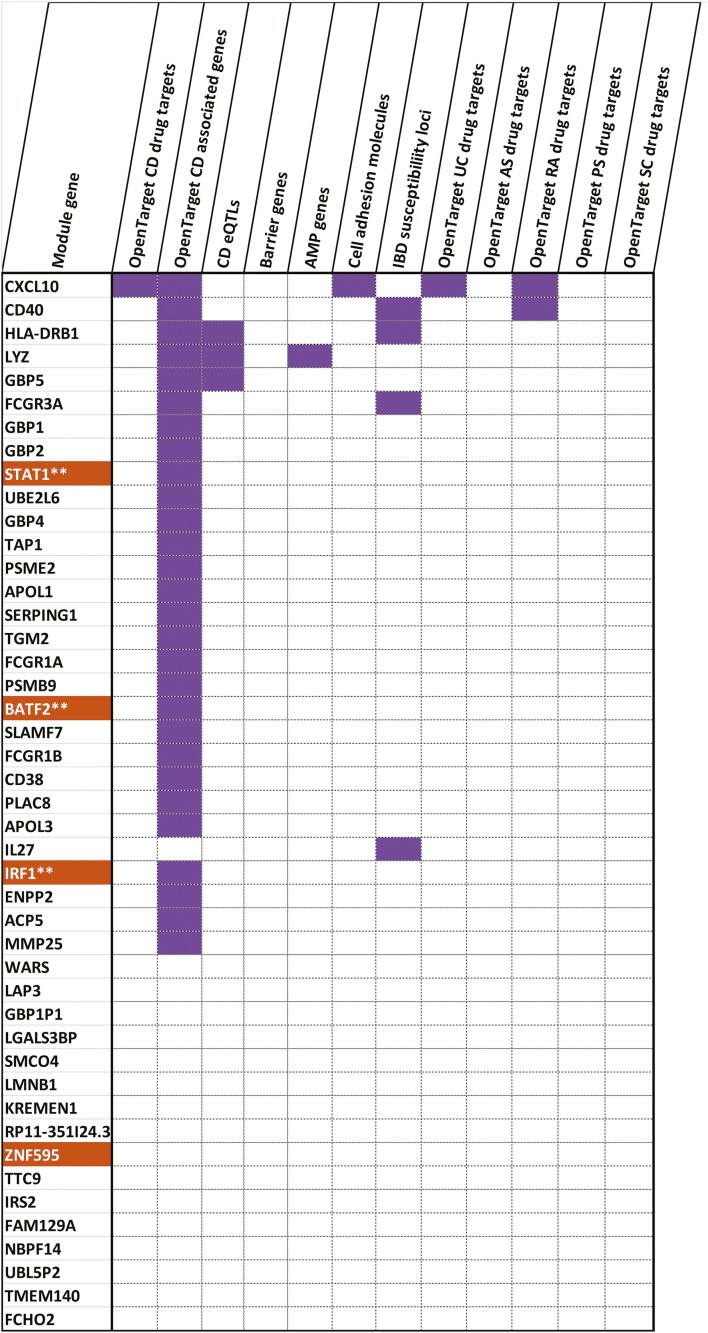
FIGURE 5.
The functional profile of the genes in the monocyte-gene expression derived module 9 active across the disease behavioral phenotype. Sixty-four percent of the module 9 hubs were annotated as being targets of drugs used to treat intestinal inflammatory disorders such as CD and UC, other inflammatory disorders such as ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and sclerosing cholangitis, associations with CD, role as CD eQTLs or genes relevant to CD in terms of their activity (antimicrobial peptide functions, barrier functions, chemokine functions and cell adhesion). Genes marked in orange denote transcription factors. **Indicates TFs that are identified as being relevant regulators (of the genes in the same modules) by ChEA3.37 The figure indicates that more than half of the genes were previously identified as involved in the pathogenesis of CD as recorded in the Open Targets database.48