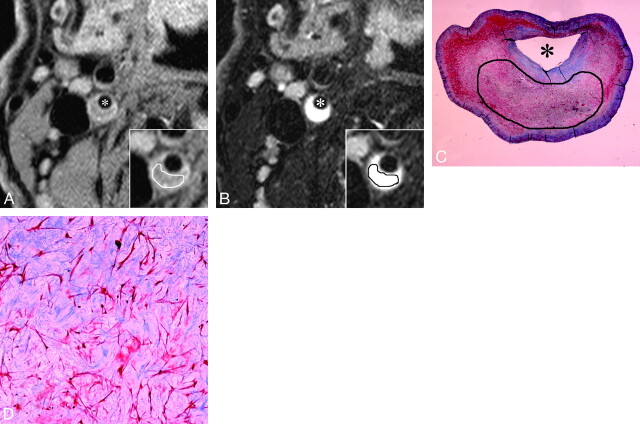
Fig 4.
A–D, An example of MR images and histopathologic features of plaque mainly consisting of myxomatous tissue. A and B, Short-axis T1- and T2-weighted images. Inset, a magnification of the atherosclerotic carotid plaque. With manual operator-defined ROI for myxomatous tissue, the rSIs on T1- and T2-weighted imaging were 1.18 and 2.0, respectively. Asterisks indicate the lumen. C and D, The low- and high-power histologic cross section (Masson trichrome stain; original magnification, 3.87 and 25) matched to axial MR images (A and B). Manual operator-defined ROI for rSI calculation is shown on low-power cross section (C). Myxomatous tissue contains pleomorphic smooth muscle cells and a large amount of extracellular matrix mainly composed of proteoglycan. Remarkable hyperintensity on T2-weighted image (B) is characteristic of myxomatous plaque, which might reflect that the extracellular matrix is associated with abundant water molecules.