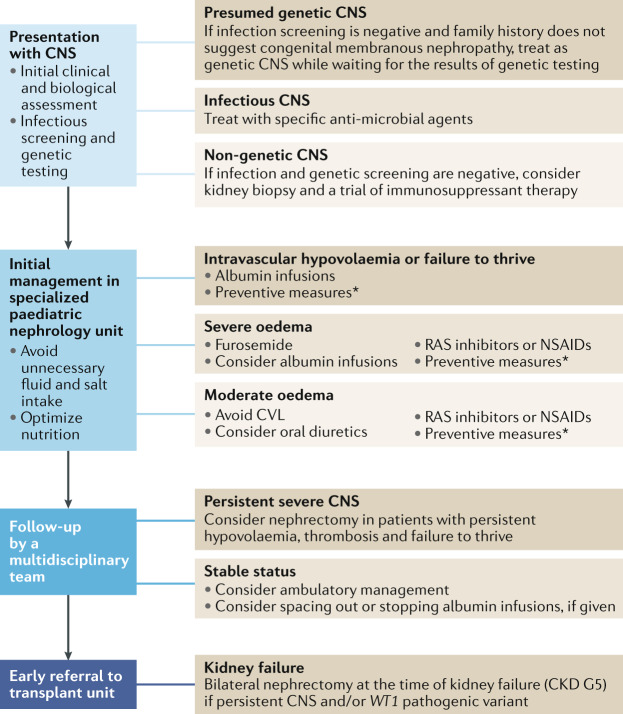
Fig. 1. Opinion-based management algorithm for CNS.
At presentation with congenital nephrotic syndrome (CNS), a clinical and biological assessment including screening for congenital infections and genetic analysis is recommended. Initial treatment should be based on the results of these assessments. Patients should be managed at diagnosis by a specialized paediatric nephrology team. Blood volume should be assessed and symptomatic treatments instituted to maintain blood volume and prevent complications. Follow-up must be managed by a multidisciplinary team. Nephrectomy can be considered for children with persistent, severe CNS despite optimal management. Stable children can be managed on an outpatient basis with spacing or even stopping of albumin infusions. All children should be referred promptly to a kidney transplant team. Bilateral nephrectomy is recommended at the time of kidney failure (chronic kidney disease (CKD) G5) if nephrotic syndrome persists and/or if the patient has a WT1 pathogenic variant. *Preventive measures: prophylaxis for thrombosis, infection and anaemia, adequate nutrition and growth hormone substitution. RAS, renin–angiotensin system, CVL, central venous line.