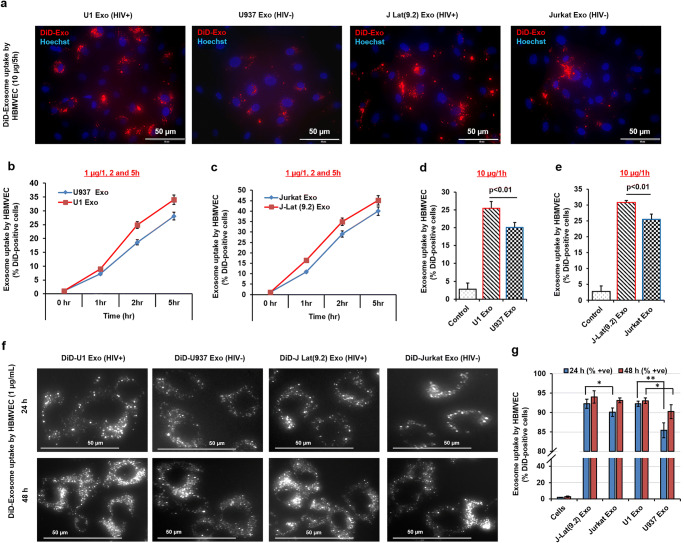
Fig. 3.
The differential uptake of exosomes isolated from uninfected and latent HIV-1 infected cells by primary HBMVECs. a Cells were exposed to DiD-label exosomes (10 μg/mL) for 5 h, washed twice with PBS, and the red fluorescence of DiD-exosomes were monitored under fluorescent microscope. The red dots indicate the uptake of DiD-exosomes by HBMVECs. b and c Using low concentrations of exosomes (1 μg/mL), the kinetics of the exosome uptake by HBMVECs with time (as indicated) was compared by detecting the number of DiD-positive cells by MACSQuant Analyzer. d and e To study high-affinity uptake, cells were incubated with 10 μg/mL exosomes for 1 h, and the exosome uptake by HBMVECs was assessed by measuring the number of DiD-positive cells by MACSQuant Analyzer. f For maximum uptake, cells were exposed to DiD-exosome (1 μg/mL) for 24 and 48 h, washed, and qualitatively measured by detecting DiD-positive cells under fluorescence microscopy, and (g) quantitatively measured by MACSQuant Analyzer. For better image quality, the brightness and contrast were adjusted uniformly within experiments using either Adobe Photoshop 7.0 or ImageJ software (version 1.50). Error bars show mean ± SD, n = 3 independent experiments per group, and significant changes are presented as p values (*p < 0.01, **p < 0.001)