FIGURE 4.
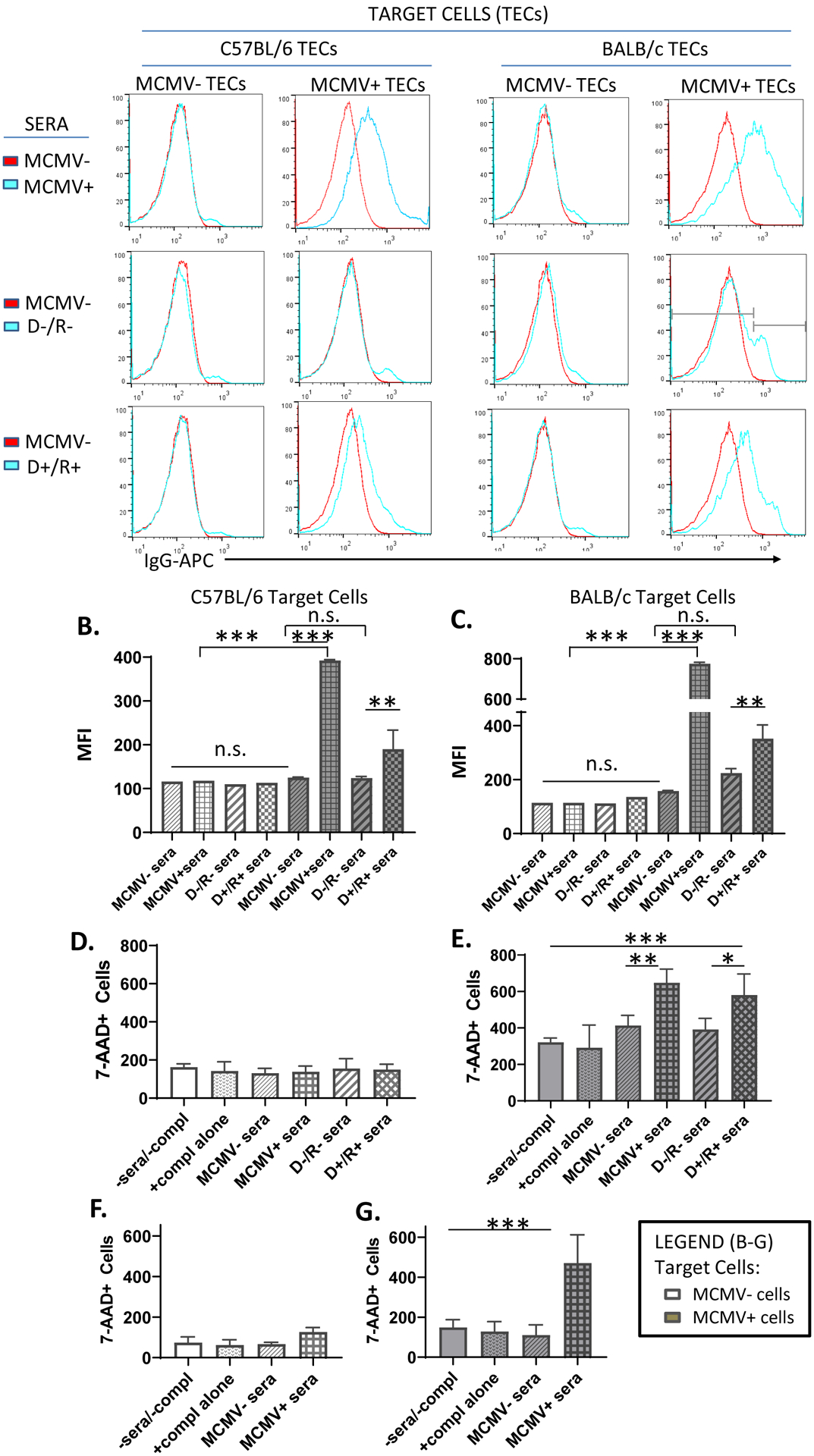
Antibody binding and complement dependent cytotoxicity of MCMV-infected target cells.
(A) Uninfected or MCMV-GFP infected B6 or BALB/c renal tubular epithelial cells (TECs) were incubated either with sera from MCMV nonimmune B6 mice (MCMV−, red lines), or from MCMV immune (MCMV+) B6 mice, D−/R− or D+/R+ recipients (blue lines). IgG binding to target cells was identified by staining with anti-mouse IgG-APC antibodies and detection by flow cytometry. Histogram subgating is shown with gray bars. (B, C) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of IgG binding was compared among groups for both uninfected (white bars) and MCMV-infected (gray bars) B6 (B) or BALB/c (C) TEC target cells.
(D-E) A complement dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) assay using uninfected (D) or MCMV-GFP infected (E) BALB/c 3T3 target cells was performed by incubation of target cells with MCMV−/+ sera or transplant sera as in (A), in the presence of rabbit complement for 3 hours. Cytotoxicity was quantitated using 7-AAD staining. Cells incubated without sera or complement (-sera/-compl) or with complement alone (+compl alone) were included as controls. (F-G). CDC assay was repeated using MCMV−/+ sera and BALB/c TEC target cells, as described for (D-E).
(A-G) All experiments were performed 3 times and representative experiments are shown.
* p<0.05; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001.
