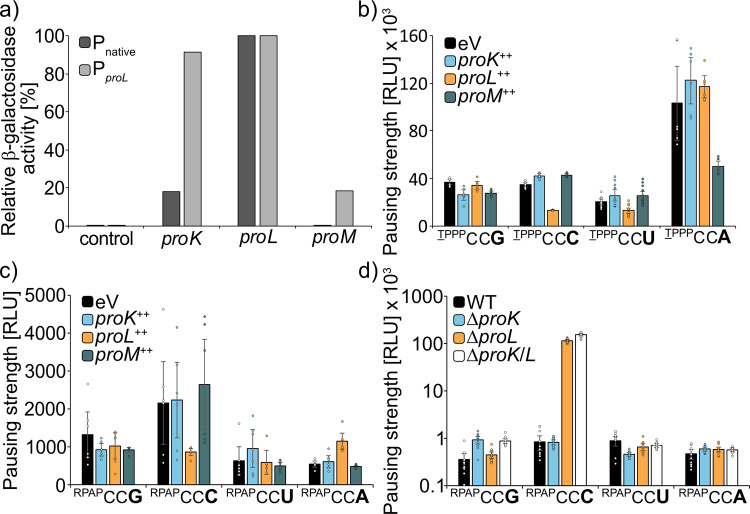
Fig. 6. Influence of prolyl-tRNA copy number on the codon-dependent pausing strength at PP-motifs.
a Approximation of E. coli BW25113 cells carrying the weak HisL*_Lux operon (TPPP) with different proline codon usage were transformed with pBBR1 MCS4-lacZ plasmids encoding ProK, ProL, or ProM under the control of their corresponding native promoters. n = 4. b E. coli BW25113 cells carrying the weak HisL*_Lux operon (TPPP) were transformed with pBBR1 MCS4-lacZ plasmids encoding for ProK, ProL, or ProM under control of PproL and tested for bioluminescence emission. n = 6. c E. coli BW25113 cells carrying the “non-PP” HisL*_Lux operon (RPAP) were transformed with pBBR1-MCS4-lacZ plasmids encoding for ProK, ProL, or ProM under control of PproL and tested for bioluminescence emission. n = 6. d The “non-PP” HisL*Lux operon (RPAP) was genomically integrated in E. coli BW25113 deletion strains lacking either proK (ΔproK), proL (ΔproL), or both (ΔproK/L) and cells were tested for bioluminescence emission. n = 12, Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals.