FIGURE 3.
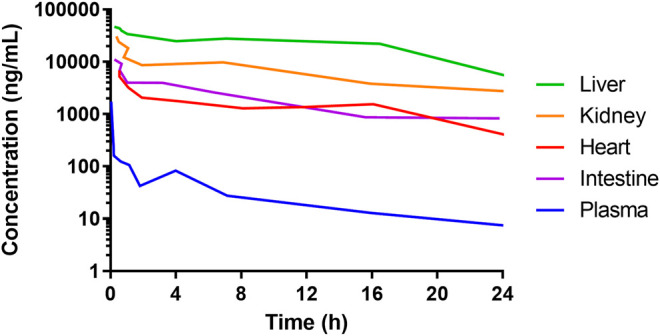
Concentrations of doxorubicin in plasma and liver, heart, kidney, and intestines of mice following 5 mg/mL intravenous administration of a solution. Data from Luo et al. (2017). The high concentration of doxorubicin in all the organs shows that the side-effects of many anti-cancer drugs are not ubiquitously dose-dependent. Rather, they are associated with the tissue-specific cell proliferation rate. This is why cancer tissue and healthy intestinal tissue are typically heavily affected.
