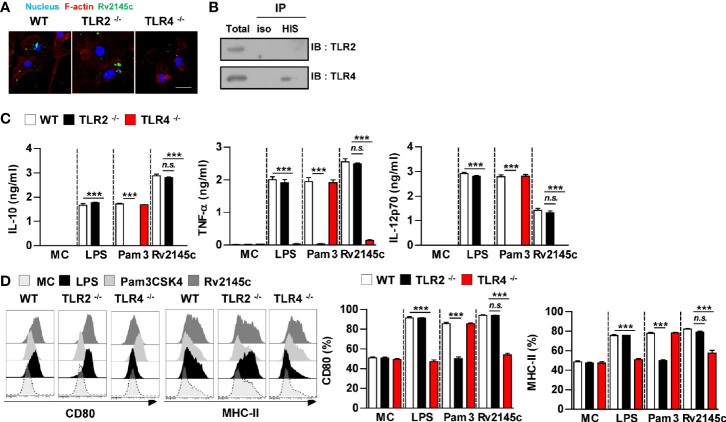
Figure 2.
Rv2145c induces macrophage activation via TLR4 pathways. BMDMs derived from wild-type (WT), TLR2–/–, and TLR4–/– mice were treated with Rv2145c (10 μg/ml), LPS (100 ng/ml), or Pam3CSK4 (Pam3) (100 ng/ml) for 24 h. (A) BMDMs-treated with Rv2145c for 1 h were fixed and then stained with DAPI (blue) and an Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated anti-Rv2145c antibody. Representative images from three independent experiments are shown. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) The lysates from BMDMs treated with Rv2145c for 6 h were used for immunoprecipitation with anti-mouse IgG or anti-His antibodies. Thereafter, proteins were detected using immunoblotting with anti-TLR2 or anti-TLR4 antibodies. The total is shown as the mean total in cell lysates (input). (C) The production of IL-10, TNF-α, and IL-12p70 in the culture supernatants was determined by ELISA. All data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n = 3). (D) Expression of CD80, and MHC class II molecules on BMDMs stimulated with each antigen was determined by staining and flow cytometry. The bar graphs show the mean percentage ± SD of each surface molecule on F4/80+ cells across three independent experiments. ***p < 0.001 for treatment values in BMDMs from TLR2-/- or TLR4-/- mice compared with those in Rv2145c-, LPS- or Pam3CSK4-treated BMDMs from WT mice. n.s., no significant difference. MC, medium controls.