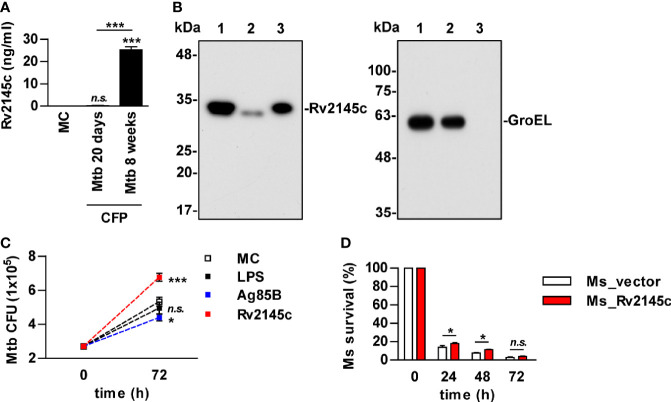
Figure 4.
Rv2145c is mainly present in the mycobacterial cell wall and promotes bacterial growth in macrophages. (A) Mtb was cultured in Sauton’s medium for 20 days and 8 weeks. The level of Rv2145c in culture filtrate proteins (CFP) was measured by indirect-ELISA. CFP was added to a plate, and then a mouse anti-Rv2145c antibody was added. HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG was then added, and TMB substrate was added and converted by HRP before detection. (B) Rv2145c in fractions from Mtb was detected by Western blot analysis using an anti-His antibody. The expression of cytosolic GroEL was detected by anti-GroEL antibody as a positive control. Lane 1: whole-cell lysate; lane 2: cytosolic fraction; lane 3: cell wall fraction. (C) BMDMs were infected with Mtb at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1 for 4 h, further treated with gentamicin to kill extracellular bacteria for 2 h, and incubated with or without 10 μg/ml Rv2145c, 100 ng/ml LPS or 5 μg/ml Ag85B for 72 h. Intracellular bacterial growth was determined by plating the cell lysates on 7H10 agar. (D) BMDMs were infected with M. smegmatis expressing Rv2145c (Ms_Rv2145c) or a vector control strain (Ms_vector) at an MOI of 10 for 4 h and further treated with gentamicin to kill extracellular bacteria for 2 h. The medium was then changed. CFU assays were conducted at the indicated times. The mean ± SD is shown for three independent experiments. *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 for the treatment compared with MC or for the difference between the treatment or vector controls (Ms_vector). n.s., no significant difference. MC, medium controls.