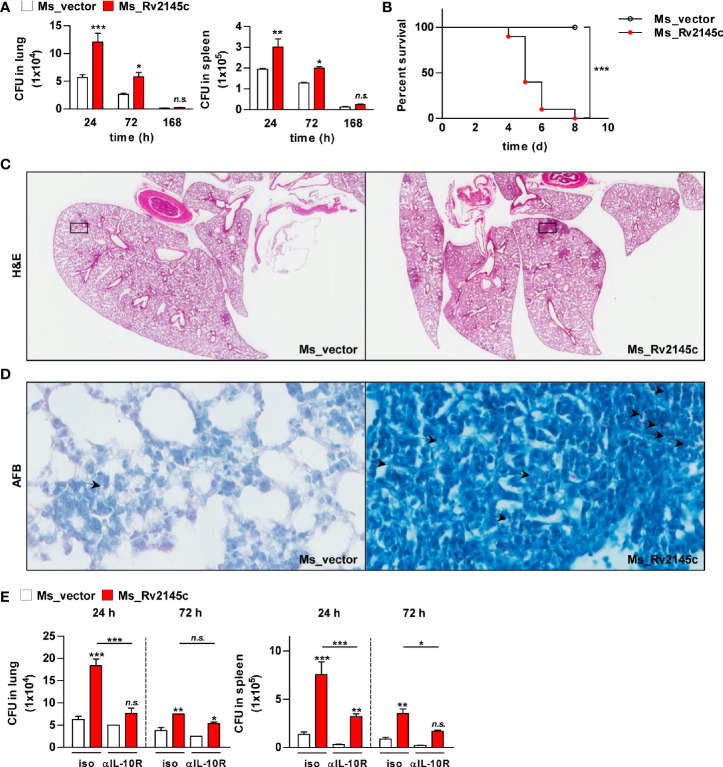
Figure 8.
Expression of Rv2145c increases virulence of M. smegmatis in vivo. (A) C57BL/6 mice (n = 3 per group at each time point) were infected intravenously with Ms_vector or Ms_Rv2145c (1 × 106 CFU/mouse). Mice were sacrificed at the indicated time points (24, 72 and 168 h), CFUs were determined in the lungs and spleens. (B) For the survival test, C57BL/6 mice (n = 5 per group) were infected intravenously at a high dose (1 × 107 CFU/mouse). (C, D) The lung tissues of Ms_vector or Ms_Rv2145c strain (1 × 106 CFU/mouse)-infected mice were collected at 72 h post infection and stained with (C) hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and for (D) acid-fast bacilli (AFB). (H&E magnification ×10, AFB magnification ×400). The granuloma area and the bacterial count from a lung section were plotted. (E) C57BL/6 mice (n = 3 per group at each time point) were treated with 1 mg/ml anti-IL-10R antibody or isotype control antibody intraperitoneally, and the next day, they were infected intravenously at a dose of 1 × 106 CFU/mouse. Mice were sacrificed at the indicated time points (24 and 72 h), and CFUs were determined in the lungs and spleens. The mean ± SD is shown for three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 compared vector controls or difference between treatment data. Treatments with no significant effect are indicated as n.s.