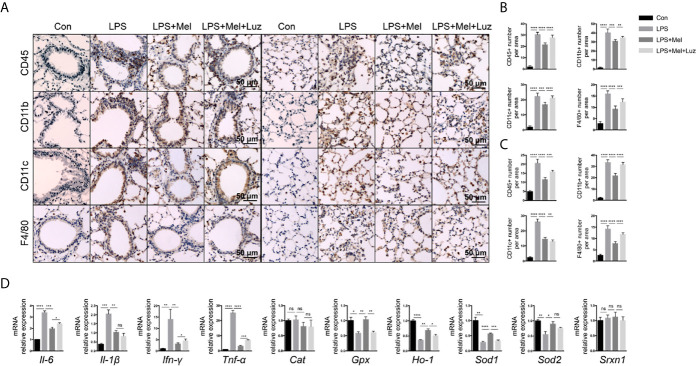
Figure 3.
Presenting melatonin at histochemical and RNA levels inhibits chronic inflammation in the lungs of mice exposed to LPS. (A–C) Significantly fewer CD45+ T cells, CD11b+ and CD11c+ and F4/80+ macrophages infiltrated into mouse lung bronchi and alveoli when LPS-exposed mice were given melatonin orally daily than non-treated mice. Luzindole (MT1/MT2 inhibitor) increased the infiltration of these inflammatory cells into the mouse lung, even when the mice were treated with melatonin. N = 5–7. (D) Mice treated with melatonin expressed lower levels of Il-6, Il-1β, Ifn-γ, and Tnf-α mRNAs as well as more Gpx, Ho-1, Sod1, and Sod2 mRNAs in the lungs than compared with LPS-exposed mice. Mice treated with luzindole (MT1/MT2 inhibitor) along with melatonin had higher levels of Il-6, Ifn-γ, and Tnf-α and decreased Gpx, Ho-1, and Sod1 mRNA expression in the lungs. N = 4–5. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, ns, no significance.