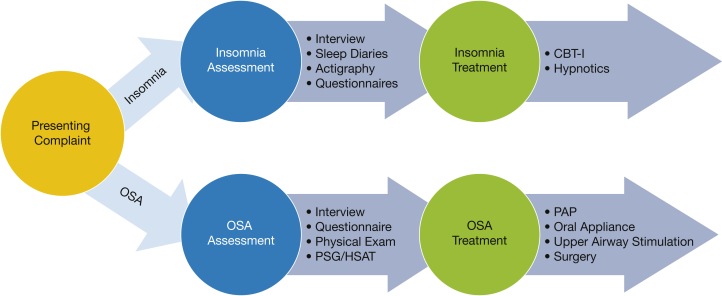
Figure 1.
This figure illustrates the traditional model for clinical management of comorbid insomnia and sleep apnea (COMISA). The presenting complaint or reason for referral serves as the basis for provisional diagnosis (insomnia or OSA) which then leads to parallel clinical pathways. If insomnia is suspected, the assessment typically involves a clinical interview with sleep diaries, actigraphy, and questionnaires used as appropriate. The standard treatment is CBT-I with short-term use of hypnotic medications appropriate in certain situations. If OSA is suspected, the assessment typically involves a clinical interview and examination followed by a PSG or HSAT, with questionnaires used as needed. The standard treatment is PAP, with other treatments such as oral appliance, upper airway stimulation, or surgery considered when appropriate. CBT-I = cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia; HSAT = home sleep apnea test; PAP = positive airway pressure; PSG = polysomnography.