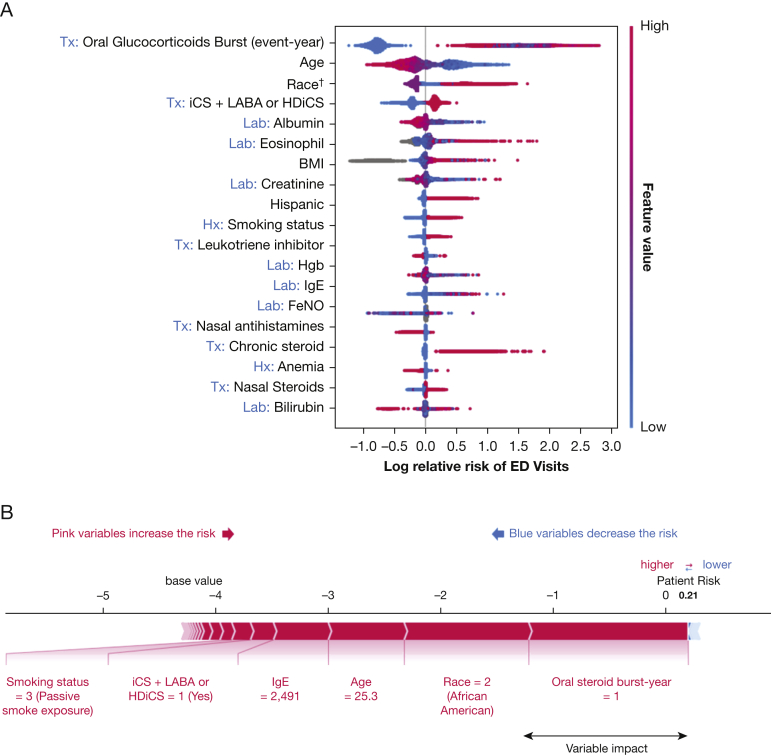
Figure 2.
A, B, Prediction model of ED visits. Interpretation of model built with gradient-boosting machine algorithm. A, Top 3 risk factors are the need for oral glucocorticoid bursts, younger age, and Black race: present (pink) increased the risk of ED visit, whereas absent (blue) decreased it. B, Predicted high-risk patient that explained, with additive factors of variables, the width of bar indicated relative impact of one variable. †Race: 0 = other, 1 = White, 2 = Black, and 3 = Asian. ‡Smoking status: 0 = other, 1 = never smoker, 2 = active smoker, and 3 = former smoker. Tx variables were 1 = present or 0 = absent. Lab variables were the value of the tests. FeNO = fractional exhaled nitric oxide; GERD = gastroesophageal reflux disease; HDiCS = high-dose inhaled corticosteroid; Hgb = hemoglobin; iCS = inhaled corticosteroid; Lab = laboratory; LABA = long-acting inhaled β-agonist; SHAP = shapley additive explanation; Tx = treatment.