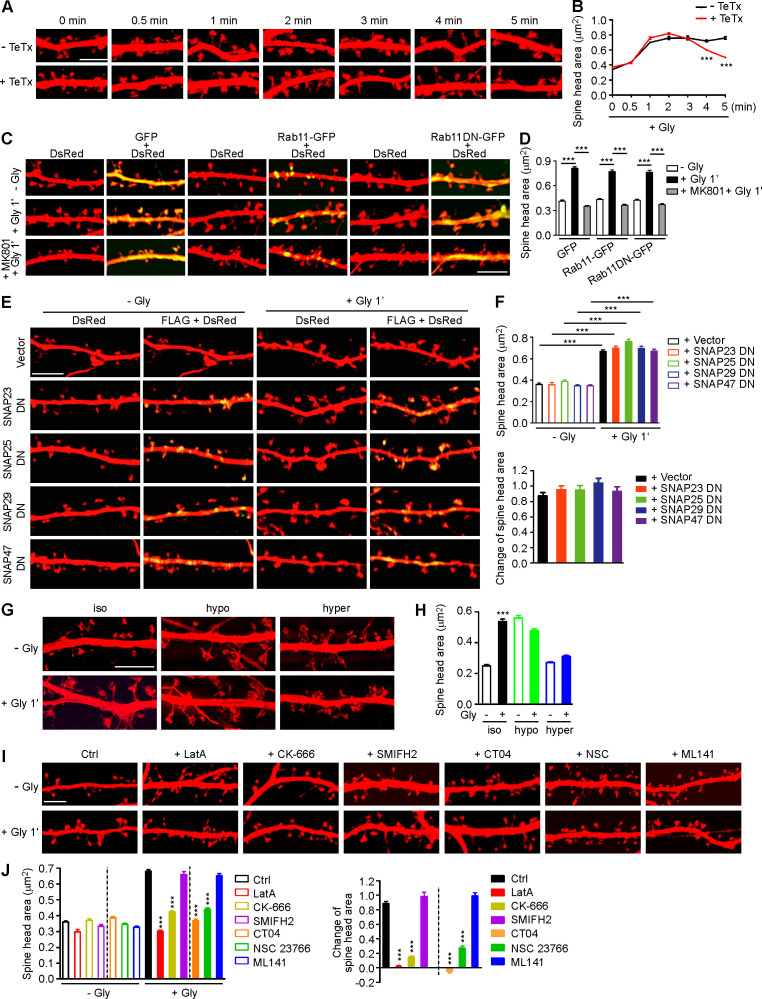
Figure S1.
Membrane unfolding and branched actin polymerization are required for initiation of sLTP. (A) Mouse hippocampal neurons transfected with pLL3.7-DsRed on DIV12 were pretreated with DMSO or tetanus toxin (TeTx) for 10 min before cLTP induction with glycine on DIV16. Neurons were fixed at different time points after glycine application and imaged by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 5 µm. (B) Quantification of spine size in A. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM at each point (− TeTx: n = 12, n = 531 for 0 min; n = 12, n = 536 for 0.5 min; n = 15, n = 685 for 1 min; n = 13, n = 558 for 2 min; n = 12, n = 538 for 3 min; n = 15, n = 675 for 4 min; n = 14, n = 580 for 5 min + TeTx: n = 14, n = 561 for 0 min; n = 14, n = 546 for 0.5 min; n = 14, n = 549 for 1 min; n = 15, n = 642 for 2 min; n = 15, n = 687 for 3 min; n = 15, n = 698 for 4 min; n = 15, n = 588 for 5 min). P values were calculated using two-tailed unpaired t test. ***, P < 0.001. (C) Mouse hippocampal neurons were transfected with pLL3.7-DsRed and expression construct for GFP fusion of Rab11 WT or DN (S25N) mutant on DIV12 and pretreated with DMSO or MK801 before cLTP induction on DIV16. Neurons were fixed 1 min after glycine application and imaged by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 5 µm. (D) Quantification of spine size in C. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM for each group (GFP: n = 10, n = 222 for − Gly; n = 11, n = 274 for + Gly; n = 10, n = 228 for + MK801 + Gly; Rab11-GFP: n = 11, n = 273 for − Gly; n = 10, n = 220 for + Gly; n = 11, n = 236 for + MK801 + Gly; Rab11DN-GFP: n = 10, n = 228 for − Gly; n = 11, n = 234 for + Gly; n = 11, n = 237 for + MK801 + Gly). P values were calculated using one-way ANOVA by Newman–Keuls post hoc test. ***, P < 0.001. (E) Mouse hippocampal neurons transfected with pLL3.7-DsRed and expression construct for FLAG-tagged SNAP DN mutant on DIV12 and induced cLTP on DIV16. Neurons were fixed 1 min after glycine application, immunostained with antibodies to FLAG, and imaged by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 5 µm. (F) Quantification of spine size in E. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM for each group (vector: n = 10, n = 378 for − Gly; n = 11, n = 391 for + Gly; SNAP23 DN: n = 11, n = 374 for − Gly; n = 11, n = 386 for + Gly; SNAP25 DN: n = 10, n = 364 for − Gly; n = 11, n = 394 for + Gly; SNAP29 DN: n = 11, n = 393 for − Gly; n = 11, n = 385 for + Gly; SNAP47 DN: n = 11, n = 379 for − Gly; n = 11, n = 382 for + Gly). P values were calculated using one-way ANOVA by Newman–Keuls post hoc test. ***, P < 0.001. (G) Effect of osmotic shock on spine enlargement 1 min after glycine application. Neurons were pretreated with iso-osmotic, hypo-osmotic, or hyperosmotic solution, respectively, for 10 min, and cLTP was performed in the same solution on DIV16. Neurons were fixed 1 min after glycine application and imaged by 3D-SIM microscopy. Scale bar, 4 µm. (H) Quantification of spine size in G. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM for each group (iso: n = 14, n = 388 for − Gly; n = 12, n = 382 for + Gly; hypo: n = 14, n = 398 for − Gly; n = 15, n = 488 for + Gly; hyper: n = 14, n = 464 for − Gly; n = 13, n = 434 for + Gly). P values were calculated using two-tailed unpaired t test. ***, P < 0.001. (I) Effects of inhibitors for actin remodeling regulators on spine enlargement 1 min after glycine application. Shown are representative confocal images. Scale bar, 5 µm. CK-666, Arp2/3 inhibitor; SMIFH2, formin inhibitor; CT04, RhoA inhibitor; NSC 23766, Rac1 inhibitor; ML141, Cdc42 inhibitor. (J) Quantification of spine size (left) and changes in spine size (right) in I. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM for each group (Ctrl: n = 13, n = 523 for − Gly; n = 13, n = 537 for + Gly. LatA: n = 12, n = 516 for − Gly; n = 12, n = 519 for + Gly; CK-666: n = 13, n = 520 for − Gly; n = 13, n = 533 for + Gly; SMIFH2: n = 13, n = 552 for − Gly; n = 13, n = 561 for + Gly; CT04: n = 13, n = 546 for − Gly; n = 13, n = 522 for + Gly; NSC 23766: n = 13, n = 524 for − Gly; n = 14, n = 562 for + Gly; ML141: n = 13, n = 532 for − Gly; n = 13, n = 530 for + Gly). P values were calculated using one-way ANOVA by Newman–Keuls post hoc test. ***, P < 0.001 when compared with Ctrl.