Extended Data Fig. 3 |. Ac4C in eukaryotic cells with manipulated NAT10 expression.
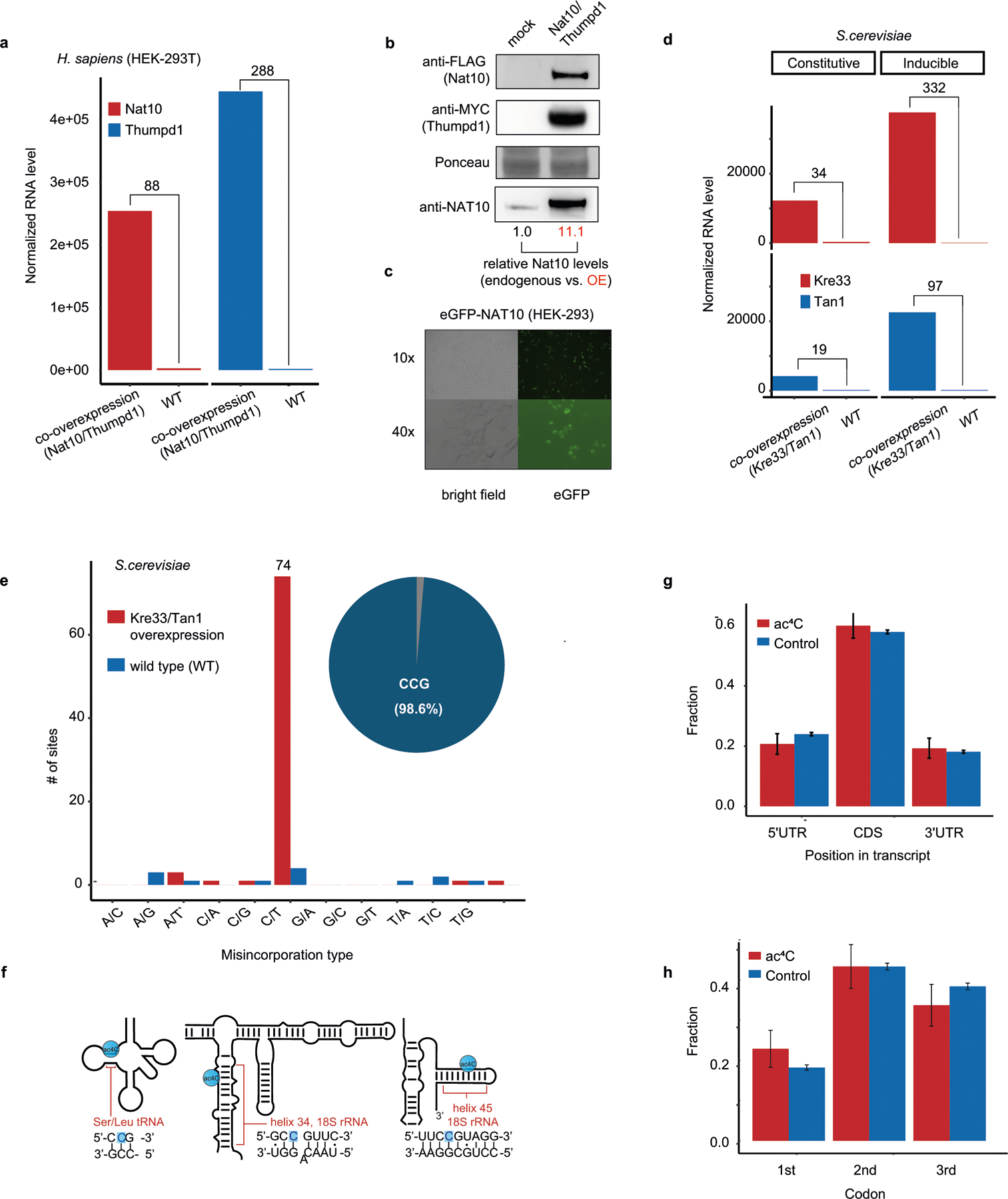
a, RNA expression of NAT10 and THUMPD1 in HEK-293T cells overexpressing both genes compared to wild-type cells. Shown are TMM-normalized read counts. The numbers above the bars indicate fold increase compared with the wild type. b, Immunoblotting analysis of NAT10 and THUMPD1 overexpression in HEK-293T cells. Representative of 3 independent experiments with similar results. For gel source data, see Supplementary Data 3. c, Microscopy images of the eGFP–NAT10 construct, confirming nuclear and nucleolar localization of ectopically expressed N-terminally tagged protein. Representative of 3 independent experiments with similar results. d, RNA expression of Kre33 and Tan1 in wild-type yeast cells and in cells stably overexpressing Kre33 and either stably or inducibly overexpressing Tan1. The numbers above the bars indicate fold increase from the wild type. e, The number of sites displaying each of the 12 possible misincorporation patterns are displayed (bar plot, y axis) for sites found in poly(A)-enriched RNA from both wild-type S. cerevisiae cells and S. cerevisiae cells overexpressing both Kre33 and Tan1. The pie chart displays the proportion of sites harbouring C>T misincorporations that were embedded within a CCG motif (73 out of 74, 98.6%). f, Schematic of the known ac4C sites in human tRNAs (Leu and Ser) and in helix 34 (C1337) and helix 45 (C1842) of human 18S rRNA. The acetylated cytidine residue (highlighted in blue) is embedded within a CCG motif in all known sites. g, Fraction of ac4C sites found within the 5′ UTR, CDS and 3′ UTR (CDS, coding sequence; UTR, untranslated region). Results are shown for the set of ac4C sites in mRNA of HEK-293T cells overexpressing NAT10 and THUMPD1 (red bars, n = 139), and—as controls—for all CCG motifs present within all genes within which any ac4C was found (blue bars, n = 6,129). Error bars representing standard distribution of the binomial distribution. Data are based on 2 biologically independent samples. h, Fraction of ac4C sites at the first, second and third position of each codon, shown for ac4C sites and controls as in g. Data are mean ±s.d. of the binomial distribution and are based on two biologically independent samples.
