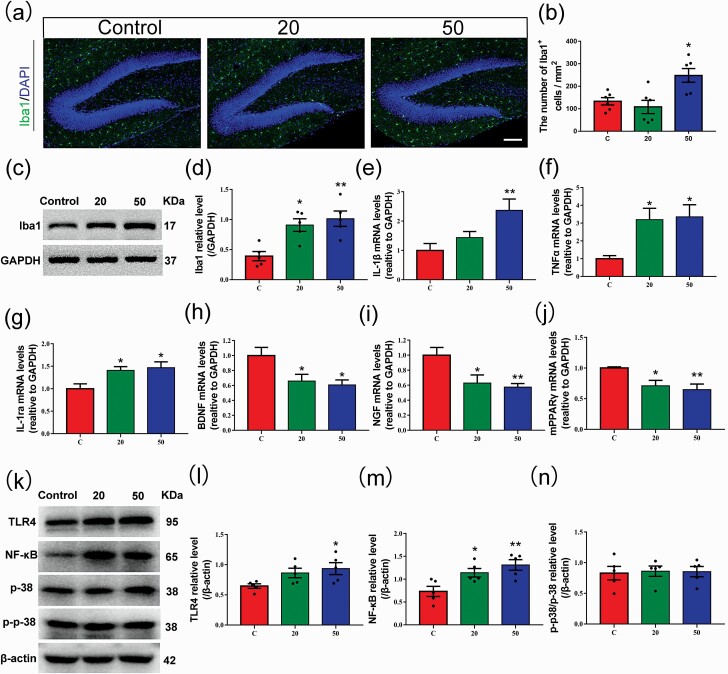
Figure 5.
Effects of gossypol exposure on microglia and inflammation-related indicators in the hippocampus at P21. (a) Representative immunofluorescence analysis of microglia using Iba1 as a marker in the hippocampus at P21. (b) Quantification of the number of Iba1+ cells in the hilus. Gossypol increased the density of activated microglia. (c), Representative western blots of Iba1 and GAPDH and densitometric quantification of protein levels in the hippocampus at P21. (d) Relative Iba1 protein levels. Iba1 expression was increased following gossypol exposure. IL-1β (e), TNFα (f), IL-1ra (g), BDNF (h), NGF (i), and mPPARγ (j) mRNA levels in the hippocampus. Gossypol increased pro-inflammatory cytokine expressions, while the expressions of mPPARγand trophic factors were decreased in mouse offspring. (k) Representative western blots of TLR4, NF-κB, p-38, p-p-38, andβ-actin and densitometric quantification of protein levels in the hippocampus at P21. Relative protein levels of TLR4 (l), NF-κB (m), and the ratio of phosphorylation of p38 and p38 (n). Expressions of TLR4 and NF-κB were increased following gossypol exposure. Data represent the mean ± SEM. (b) n = 10 per group, 10 sections from 5 offspring in each group. (d, l–n) n = 5 per group, 5 offspring from 5 dams in each group. (e–j) n = 10 per group, 10 offspring from 5 dams in each group. *P < .05 and **P < .01 compared with the controls.