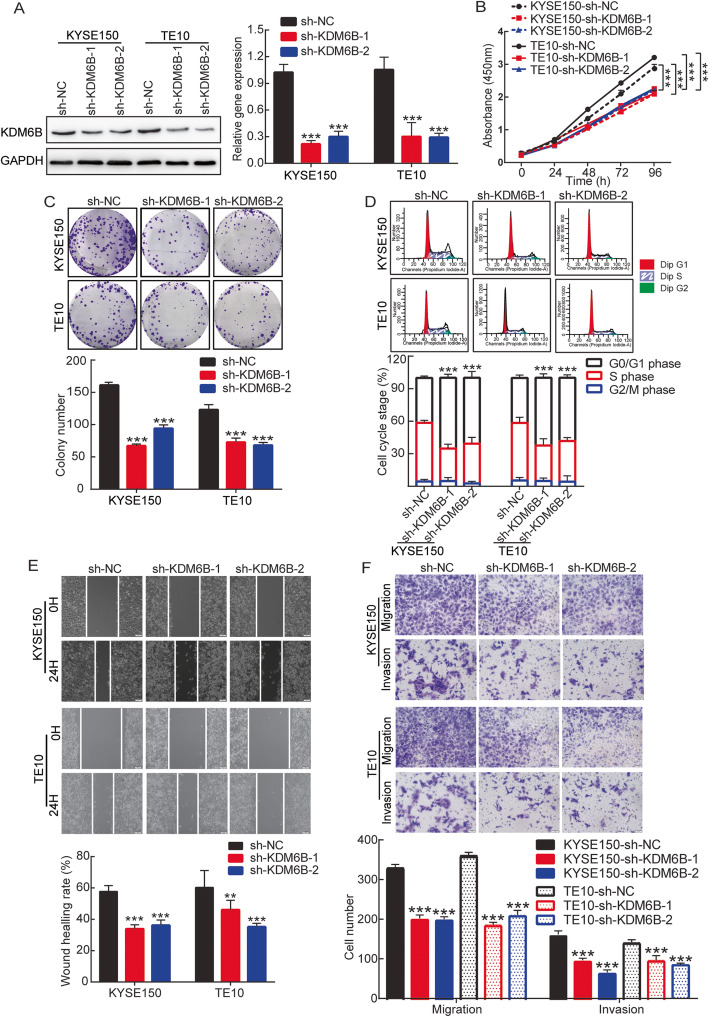
Fig. 2.
The knockdown of KDM6B KDM6B inhibites the proliferation and Metastasis of ESCC cells. a Western blotting (left panels) and RT-qPCR (right panels) were performed to measure the KDM6B protein and mRNA expression level changes following KDM6B interference. b The CCK-8 assay was used to determine cell viability after interfering KDM6B every 24 h for 4 days. c ESCC cells were seeded at a density of 500 cells/well for clone formation assays. Representative crystal violet staining of clone formation (upper panels) and statistical graphs of clone numbers (lower panels). d Cell cycle distribution was analyzed following the silencing of KDM6B in KYSE150 and TE10. Representative images of cell cycle distribution (upper panels) and statistical graphs of cell cycle changes (lower panels). e Cell migration was determined using the wound healing migration assay (magnification, × 100) Representative images of KYSE150 and TE10 lentivirus stable transfected at 0 and 24 h of wound healing assay, image j was used to analyze the results of wound scratch images. A bar graph shows the quantitative results of scratch healing. f Cell migration or invasion was determined using Transwell migration or invasion assay. Representative images of crystal violet stained for lentivirus stable transfected of KYSE150 and TE10 by transwell migration or invasion assays (upper panels). A statistical graph shows Cell number (lower panels). Results are representative of three independent experiments and are expressed as the mean ± S.D. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001