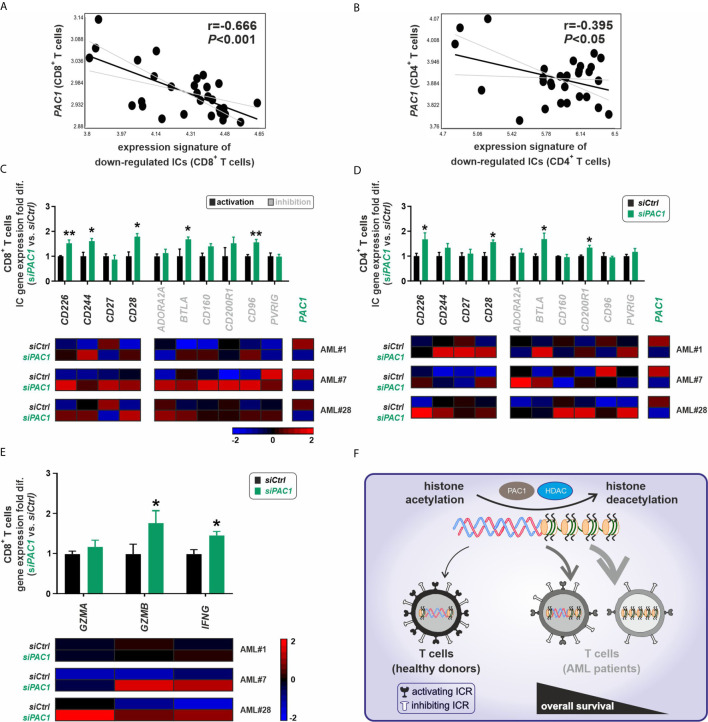
Figure 5.
Epigenetic silencing of immune-checkpoint receptors in T cells is modulated via PAC1. (A, B) Correlation analysis of the gene expression signature for downregulated ICs vs. expression pattern of PAC1 gene, in CD8+ or CD4+ T cells respectively (n=30 AML patients). (C, D) Gene expression profile of 10 downregulated IC receptors in CD8+ or CD4+T cells of AML patients upon PAC1 gene silencing. The fold differences were calculated as the ratio of siPAC1 vs. siCtrl (n=3 AML patients per each group of CD8+ or CD4+ T cells). (E) Expression profile of key effector molecules of CD8+ T cells upon PAC1 gene knockdown (n=3 AML patients). (F) BM-infiltrating T cells in AML are dysfunctional due to a downregulation of activating IC receptors mainly via a pathologic epigenetic silencing through histone deacetylation; ICR, immune checkpoint receptor; HDAC, histone deacetylase. Statistics: student’s t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.