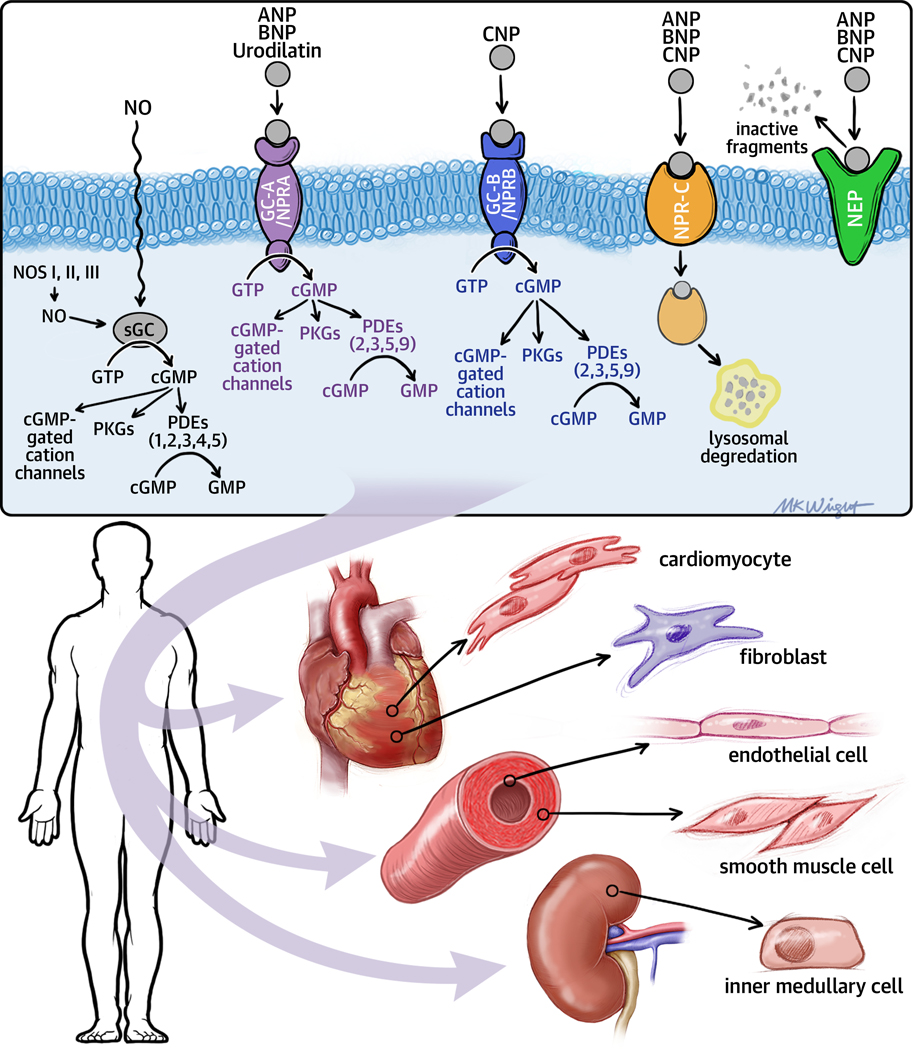
Figure 2. Natriuretic peptides and particulate (pGC) and soluble (sGC) guanylyl cyclase signaling pathways.
The natriuretic peptide system consists of five structurally similar peptides: ANP, urodilatin (an isoform of ANP), BNP, C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP), and dendroaspis natriuretic peptide (DNP). Natriuretic peptides bind to GC-A/NPRA and/or GC-B/NPRB (membrane-bound/particulate guanylate cyclases [pGCs]) and activate the signaling pathways of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). The GC-A/NPRA receptor preferentially binds ANP and BNP, and the GC-B/NPRB receptor preferentially binds CNP. Both NPR-A and NPR-B are coupled to particulate particulate guanylate cyclase. Nitric oxide (NO) binds to soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) in the cytoplasm, inducing cGMP production and activation of cGMP signaling pathways. Once the intracellular concentration of cGMP increases, cGMP-gated cation channels, cGMP-dependent protein kinases generate important biological responses in different tissues. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDEs) hydrolyze cGMP thus inhibiting signal transduction. The PDEs are comprised of a superfamily of 11 diverse isozymes (numbered PDE1, PDE2, etc) that are compartmentalized within the cell. PDE5 is primarily expressed in the vascular smooth muscle cells and catabolizes cGMP generated by soluble guanylate cyclase. PDE9 also catabolizes cGMP, but is primarily expressed in the gastrointestinal tract, kidney and brain and catabolizes cGMP generated by particulate guanylate cyclase. The natriuretic peptides are degraded by two major mechanisms: natriuretic peptide C receptor (NPR-C) –mediated internalization, followed by lysosomal degradation and enzymatic degradation by neutral endopeptidase (NEP) 24.11 (neprilysin), which is widely expressed in which is widely expressed in multiple tissues, where it often is co-localized with angiotensin converting enzyme. (Other abbreviations: ANP- atrial natriuretic peptide, BNP- brain (B-type) natriuretic peptide, CNP –C type natriuretic peptide, GC-A, particulate guanylyl cyclase A; GC-B, particulate guanylyl cyclase B; GTP, guanosine triphosphate; NOS, nitric oxide synthase; NPRA – natriuretic peptide receptor A, NPRB – natriuretic peptide receptor B, NPRC – natriuretic peptide receptor C)