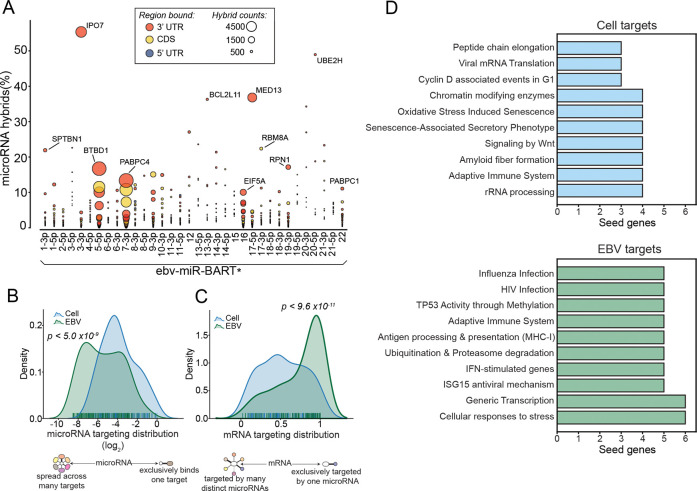
Fig 6. γHV miRNAs target components of immune signaling pathways.
(A) SNU719 hybrids containing EBV miRNAs. Each interaction was represented by a circle; circle size corresponds to the total number of hybrids formed (); The y-axis values represent the percent of all hybrids that contain the indicated miRNA, . (B) The distribution of y-axis values from (A), extended to all hybrids. Cellular and viral hybrids were compared; P-value was generated using the KS test. (C) The fraction of individual miRNAs hybridizing with each mRNA, , comparing viral and human distributions; P-value was generated using the KS test. (D) Pathways targeted by EBV and cellular miRNAs. Protein-protein interaction networks of each of the top 20 EBV or cellular target genes were obtained from StringDB[53], and resulting protein names were submitted to Enrichr[54] for pathway enrichment analysis (interrogating pathways included in the Reactome database). All statistically significant pathways (FDR < 0.05) were assigned to the target gene.