Figure 1.
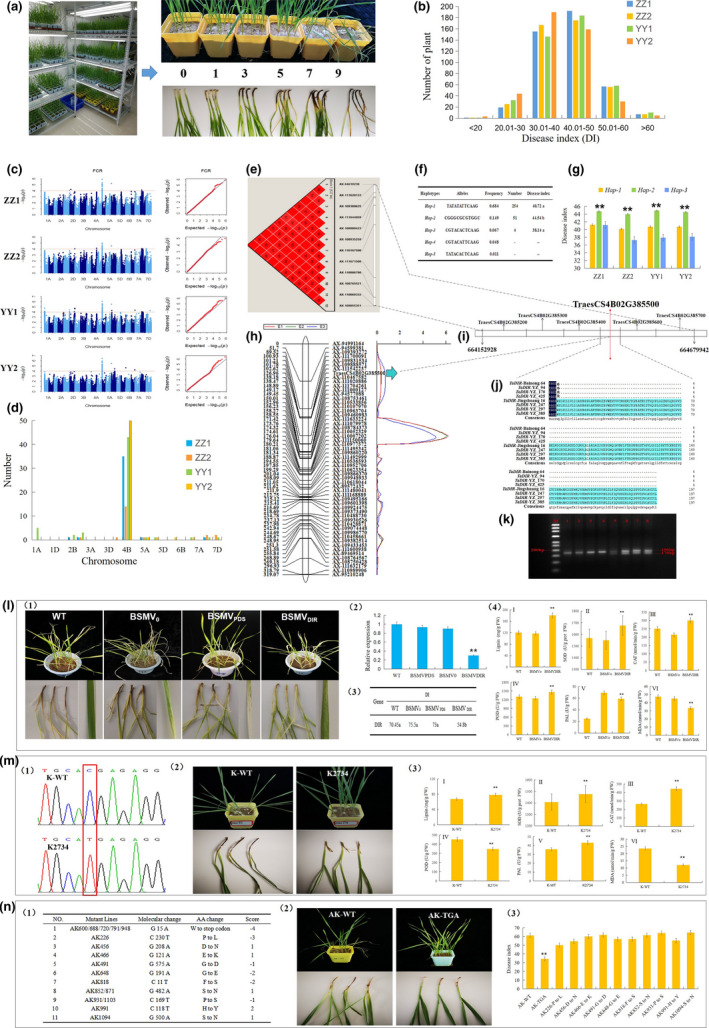
The TaDIR gene was identified by GWAS and QTL mapping of Fusarium crown rot (FCR) resistance and was functionally verified by VIGS and analysis of tetraploid and hexaploid wheat mutants. (a): Classification of FCR disease index in the surveyed cultivars. (b) Number of accessions with different FCR DI in the association panel. (c) Manhattan and Q‐Q plots for FCR DI in different environments. (d) Distribution of significant SNPs revealed by GWAS on various chromosomes. (e) Haplotype analysis of significant SNPs on 4B identified at multiple environments. (f–g) Comparison of FCR DI of wheat accessions with different alleles in the block on 4B. (h) QTL mapping for FCR DI in the Bainong64/Jingshuang16 (BJ) population. (i) The schematic range of 6 candidate genes including TaDIR identified by haplotype analysis and QTL mapping. (j) Full alignment of amino acid of TaDIR‐B1 alleles between low DI and high DI accessions. (k) Development of the dCAPS marker to distinguish TaDIR‐B1 alleles. The 190‐bp fragment from cultivars with TaDIR‐B1a could be digested into 170 and 20 bp by the restriction enzyme BalI, while those from cultivars with TaDIR‐B1b could not be digested. (l) VIGS (virus‐induced gene silencing) experiment verified the function of TaDIR‐B1 gene. (1) The phenotypes of wild type (WT), BSMV0 and BSMV TaDIR‐B1 plants for FCR; (2) the relative expression levels; (3) the averaged DI; and (4) physiological parameters. (m) Function of TaDIR‐B1 gene was verified in Kronos mutants. (1) Mutation point of TaDIR‐B1 gene in K2734; (2) investigation of FCR DI; and (3) physiological parameters. (n) Function of TaDIR‐B1 gene was verified in AK58 mutants. (1) Summary of AK58 mutant lines with amino acid change of the TaDIR‐B1 gene by sequencing; (2) investigation of FCR DI; and (3) comparison of averaged FCR DI.
