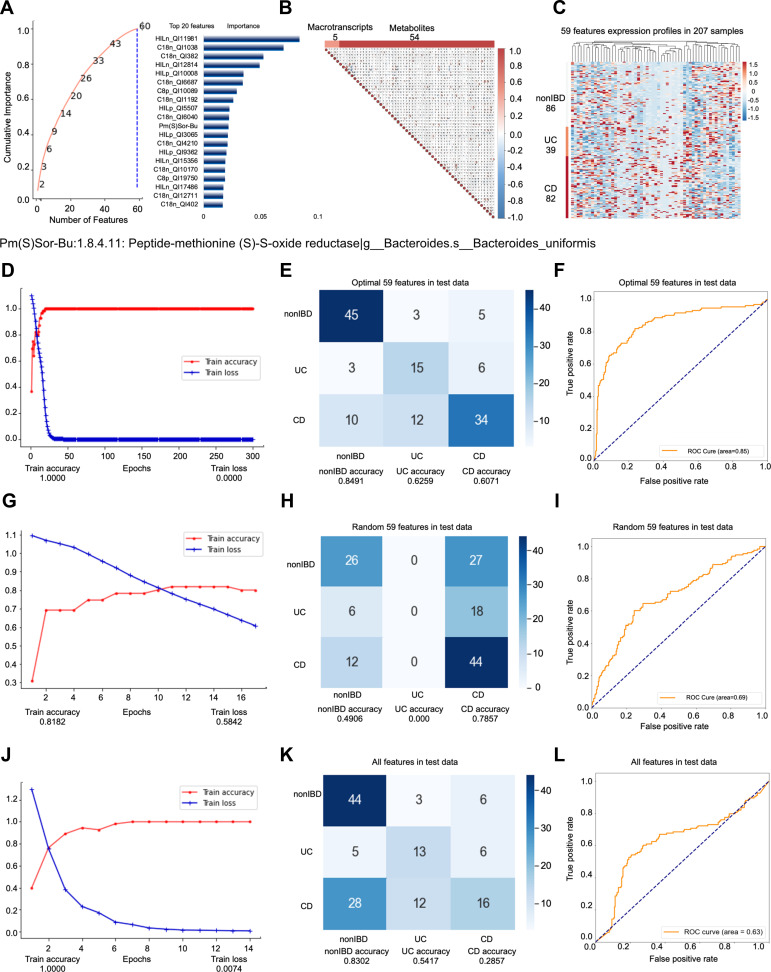
Figure 2.
Key information and results of model 2 modeling.
Notes: In the importance screening process, the cumulative importance scores of the features obtained in the third importance screening (left) and the 20 features with the highest importance scores (right) (A). The correlation between 59 features obtained through collinearity screening, 59 features including 5 metatranscripts and 54 metabolites (B). The expression of 59 features in 207 samples. The samples are arranged in the order of nonIBD, UC and CD. The distance between features is calculated using Canberra distance, and the clustering method uses complete linkage (C). Using the optimal 59 features modeling, the accuracy and the loss value of the training dataset in 300 epochs (D). The confusion matrix of the optimal 59 features (E). The AUC score of the optimal 59 features (F). Using the random 59 features modeling, the accuracy and the loss value of the training dataset in 300 epochs (G). The confusion matrix of the random 59 features (H). The AUC score of the random 59 features (I). Using the all features modeling, the accuracy and the loss value of the training dataset in 300 epochs (J). The confusion matrix of the all features (K). The AUC score of the all features (L).