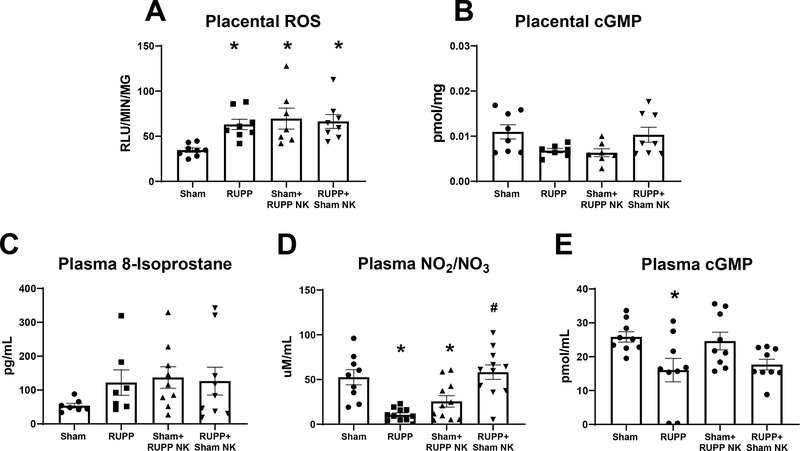
Figure 5. Effects of Natural Killer (NK) Cell Adoptive Transfer on Placental and Circulating Oxidative Stress, Cyclic GMP, and Circulating Nitrate/Nitrite levels in Pregnant Rats.
On Gestation Day (GD) 14, vehicle or 5×106 Reduced Uterine Perfusion Pressure (RUPP) NKs were infused i.v. into a subset of Sham rats and vehicle or 5×106 Sham NKs were infused i.v. into a subset of RUPP rats. On GD19, blood and placentas were collected following sacrifice and processed for further analysis. (A) Reactive oxygen species in placental homogenates were assessed using lucigenin and (B) placental cyclic GMP was measured via ELISA. (C) Circulating levels of 8-isoprostane were measured via ELISA. (D) Plasma total nitrate/nitrite was assessed using a colorimetric assay and (E) plasma cyclic GMP was measured via ELISA. All data are expressed as mean ± SEM. Sham n=7–9, RUPP n=7–11, Sham+RUPP NK n=7–10, RUPP+Sham NK n=7–10. Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons followed by Tukey’s post-hoc test. *p<0.05 versus Sham; #p<0.05 vs RUPP.