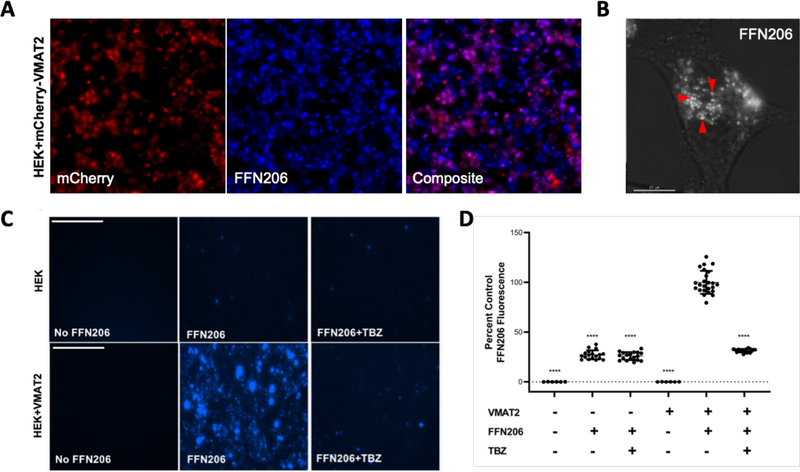
Figure 1. FFN206 packaging is dependent on VMAT2 function and maintenance of the vesicular proton gradient.
A. Representative 10x image of HEK cells stably transfected with mCherry-tagged VMAT2 (HEK+mCherry-VMAT2, left image) treated with FFN206 (center image). FFN206 fluorescence overlaps with VMAT2 fluorescence (purple, right image). B. Representative 60x TIRF microscope image demonstrates FFN206 fluorescence localized within vesicle-like compartments in a stably transfected HEK cell with VMAT2 (HEK+VMAT2), as denoted by red arrows. Scale bar = 10 μM. C. Representative images of FFN206 fluorescence in control HEK cells with and without VMAT2. In control HEK cells (top), there was no background fluorescence in the absence of FFN206 (left). FFN206 treatment exhibited minimal fluorescence (middle), and FFN206 fluorescence was unchanged following treatment with the VMAT2 inhibitor tetrabenazine (10 μM) (right). Representative images of FFN206 fluorescence in HEK+VMAT2 cells (bottom). In the absence of FFN206, no background fluorescence is observed in HEK+VMAT2 cells (left). HEK+VMAT2 cells treated with FFN206 exhibit robust fluorescence (middle) that was diminished when VMAT2 function is inhibited by treatment with 10 μM tetrabenazine (right). D. Quantification of FFN206 fluorescence from panel C. Data displayed as percent control mean and standard error of the mean, with the control group being HEK+VMAT2 cells incubated with FFN206. Each point represents one well of cells from a 96-well plate. (One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons post-hoc test **** p <0.0001 vs. control column HEK+VMAT2+FFN206).