Figure 6. Malonate induces a dynamic metabolic shift in the adult heart and promotes revascularization following MI.
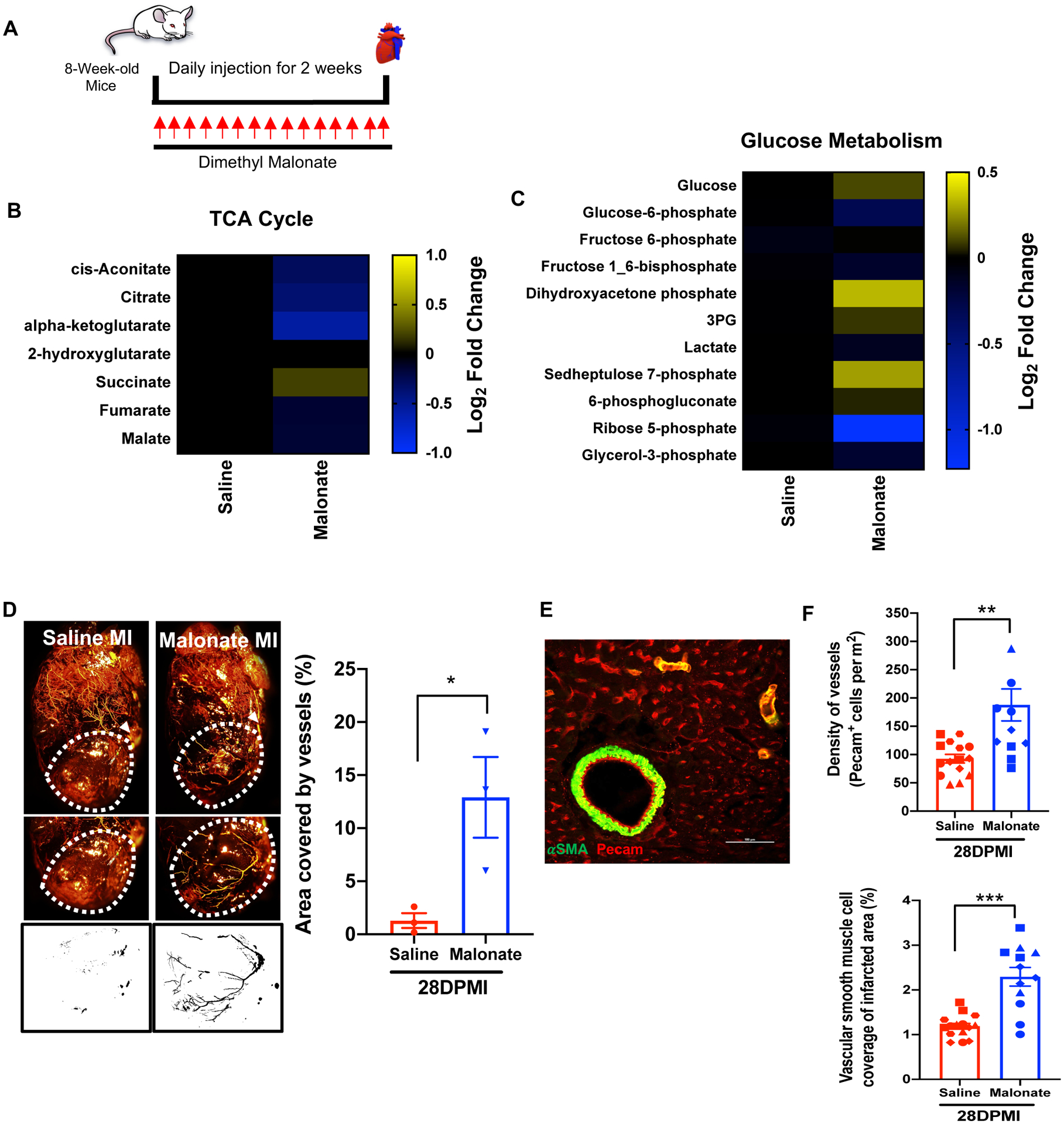
(A) Schematic of malonate administration for metabolomics. (B & C) Metabolomic changes of tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and glucose metabolism in saline and malonate treated mice at 14 days following treatment. Relative abundance of metabolites in malonate-treated mice is compared to saline-treated mice and presented as a heatmap on a log2 scale demonstrating a dynamic change in TCA cycle and glucose metabolism in malonate-treated mice. (D) Coronary vessel casting by MICROFIL injection at 28 days post-MI showing a significant increase in revascularization of the infarct zone in malonate-treated mice compared to controls. Quantification of vasculature in region of interest (ROI) by analyzing binarized images for grey level intensity by ImageJ demonstrating a significant increase in vascular density in the infarct zone. (E) Immunostaining with the endothelial marker PECAM and vascular smooth muscle cell marker α-SMA. Scale bar, 100 μm. (F) Quantification of vascular lineages demonstrating a significant increase in endothelial capillary density and vascular smooth muscle cells in the infarct zone at 28 days post-MI. (n=3–4 mice per group). *P< 0.05, **P<0.005, ***P<0.0001 by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test.
