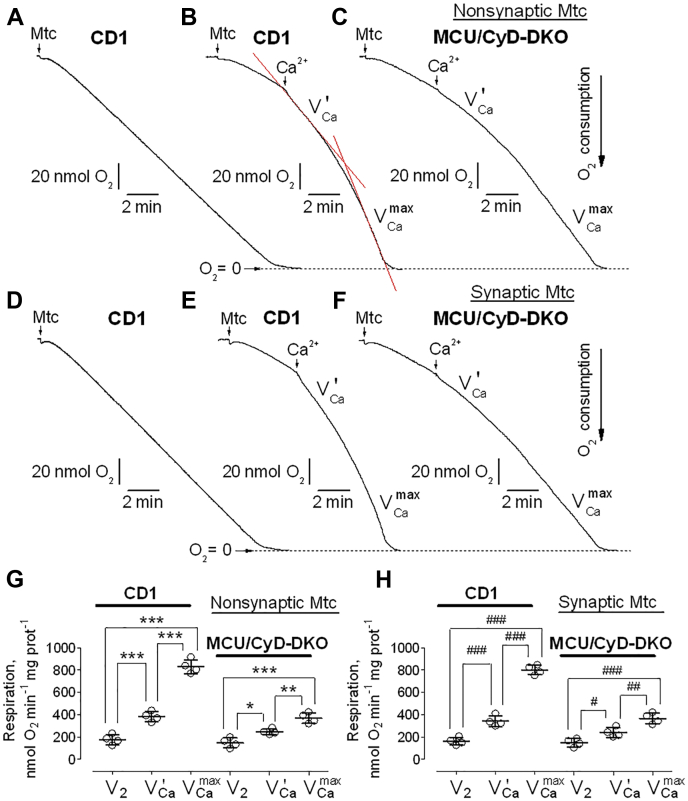
Figure 4.
Ca2+-stimulated respiration of brain nonsynaptic and synaptic mitochondria isolated from CD1 and MCU/CyD-DKO mice.A–F, representative respiratory traces of mitochondrial O2 consumption for nonsynaptic (A–C) and synaptic (D–F) mitochondria, respectively, incubated at 37 °C in the standard incubation medium supplemented with succinate (3 mM) plus glutamate (3 mM). Where indicated nonsynaptic or synaptic mitochondria (Mtc), both 60 μg of protein, were added, followed by additions of 100 μM CaCl2. A and D, the representative respiratory traces obtained with nonsynaptic (A) and synaptic (D) mitochondria isolated from brains of CD1 mice are shown. These experiments demonstrate linearity of oxygen electrode used in our study. B, C, E, and F, the respiratory rates were calculated using linear fragments of the respiratory traces (red lines) immediately after Ca2+ addition and at the maximal O2 consumption . Averaged respiratory rates are summarized for brain nonsynaptic (G) and synaptic (H) mitochondria. Data are mean ± SD from four separate experiments. ∗∗∗p < 0.001 comparing respiratory rates of nonsynaptic mitochondria from CD1 mice (ANOVA p < 0.0001, F = 117.7); ∗∗p < 0.01 comparing and respiratory rates of nonsynaptic mitochondria from MCU/CyD-DKO mice (ANOVA p < 0.0001, F = 117.7); ∗p < 0.05 comparing V2 and respiratory rates of nonsynaptic mitochondria from MCU/CyD-DKO mice (ANOVA p < 0.0001, F = 117.7). ###p < 0.001 comparing respiratory rates of synaptic mitochondria from CD1 mice (ANOVA p < 0.0001, F = 129.4); ##p < 0.01 comparing and respiratory rates of synaptic mitochondria from MCU/CyD-DKO mice (ANOVA p < 0.0001, F = 129.4); #p < 0.05 comparing V2 and respiratory rates of synaptic mitochondria from MCU/CyD-DKO mice (ANOVA p < 0.0001, F = 129.4). CyD, cyclophilin D; MCU, mitochondrial calcium uniporter; MCU/CyD-DKO, MCU/CyD-double KO.