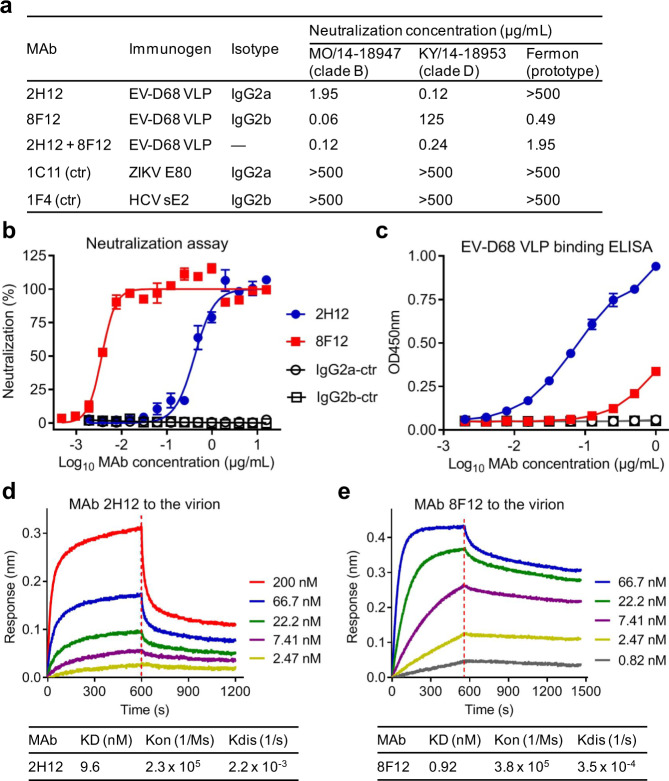
Fig. 1. Neutralization activity and binding properties of the MAbs.
a Isotypes and neutralization activity of anti-EV-D68 MAbs. Neutralization concentrations of the MAbs were defined as the lowest antibody concentrations that completely prevented virus-induced cytopathic effect. 2H12+ 8F12, MAbs 2H12, and 8F12 were combined at a ratio of 1:1. ctr, isotype control. Symbol (—), not tested. b Neutralization activity of the MAbs against EV-D68. 100 TCID50 of EV-D68 strain 18947 was incubated with two-fold serial dilutions of purified MAbs 2H12 and 8F12 for 1 h before adding to RD cells. Cell viability was measured by CellTiter-Glo 2.0 assay 3 days after infection. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of mean (SEM) of triplicate wells. c Reactivities of the MAbs towards EV-D68 VLP determined by ELISA. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) of triplicate wells. In panels (b, c), ZIKV-specific MAb 1C11 and HCV-specific MAb 1F4 served as IgG2a and IgG2b isotype controls (ctr), respectively. d, e Binding affinities of the MAbs to EV-D68 18947 virion measured by BLI. Association and dissociation steps are divided by dotted red line. MAb concentrations used and values of KD, Kon and Kdis were shown.