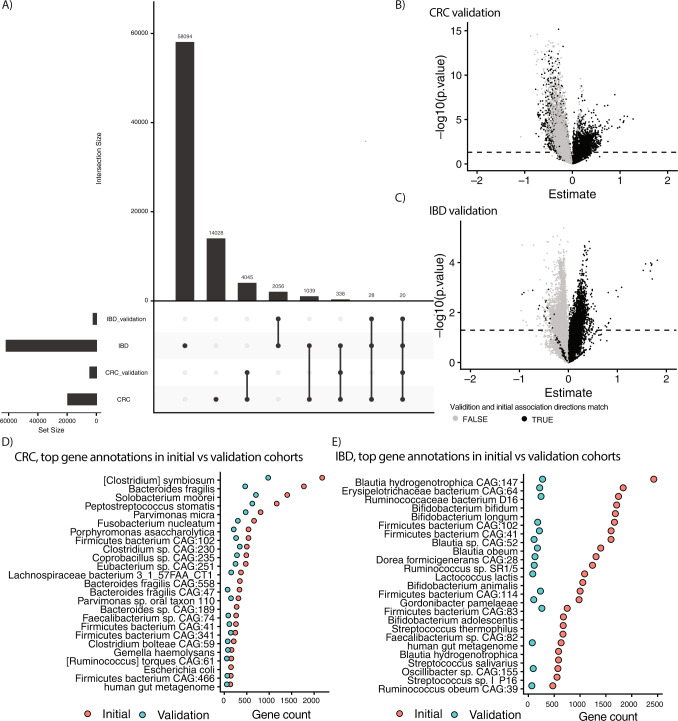
Fig. 7. Validation of gene-level architectures for CRC and IBD.
We used unadjusted, univariate linear models to test the association between gene abundance and disease state for the genes associated with IBD and CRC in two cohorts not analyzed in our initial study. A Overlaps between the initial and validation cohorts in terms of significant genes. B, C Volcano plots of CRC and IBD estimate sizes and nominal log10 P values for validation cohorts. Each point represents a different gene family. Dotted line is nominal (P value < 0.05) significance. Exact P values < 0.05 are shown above the line. Y axes are nominal log10 P values. X axes are the beta-coefficient on the binary, independent disease variable of interest. Black dots indicate the association direction (e.g., positive vs. negative) matched in the initial cohort(s), gray indicates initial, and validation associations did not have the same direction. D, E The top 25 taxonomic annotations (by frequency) of genes associated with CRC and IBD in the initial cohorts and how many of these are also found in the top 25 annotations of genes in the validation cohorts.