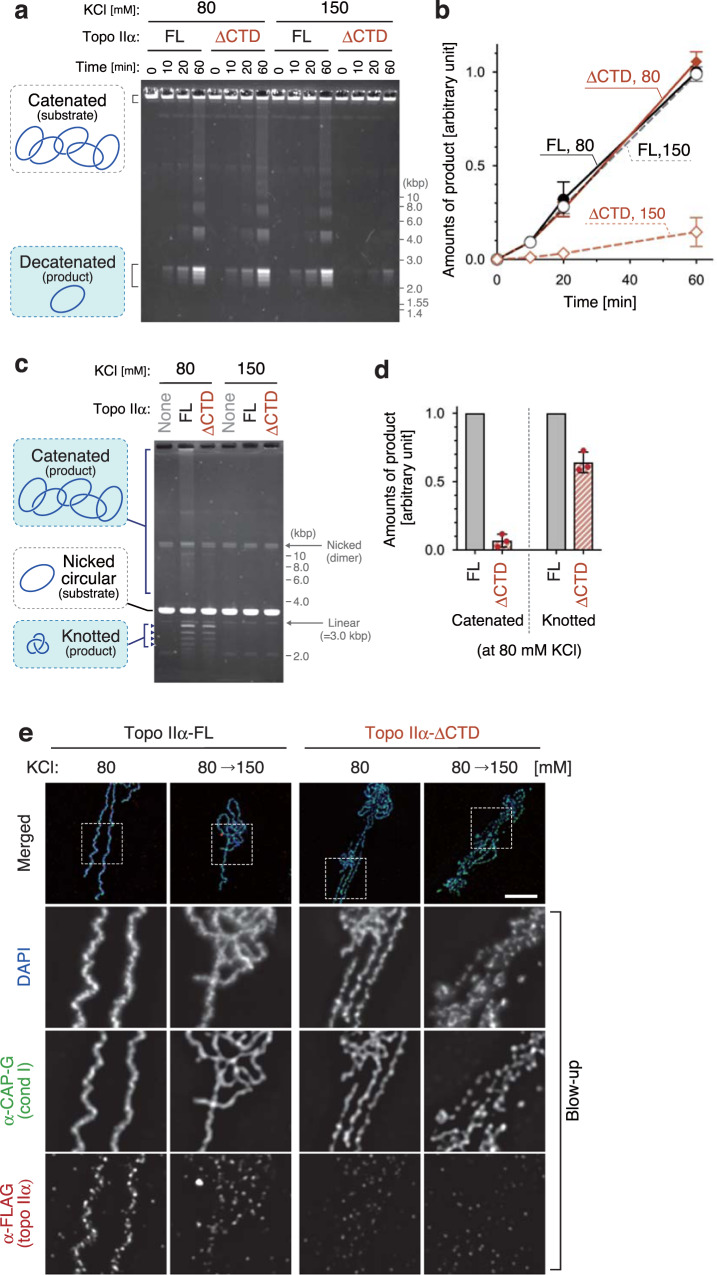
Fig. 3. Topo IIα-ΔCTD is proficient in DNA decatenation but is deficient in DNA catenation.
a, b Catenated DNA (100 ng) was mixed with a low amount (40 ng) of topo IIα-FL or topo IIα-ΔCTD in a buffer containing 2 mM ATP, 5 mM MgCl2, and either 80 mM or 150 mM KCl. After incubation at 22 °C, the resultant DNAs were recovered at the indicated time points, purified, and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. The gel was stained with ethidium bromide (a). Intensities of decatenated DNA were quantified. The mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments is shown (b). c, d Nicked circular DNA (100 ng) was mixed with an excess amount (400 ng) of topo IIα-FL or topo IIα-ΔCTD in a buffer containing 5 mM MgCl2, and either 80 mM or 150 mM KCl. After a 10-min incubation at 22 °C, the reactions were supplemented with 2 mM AMP-PNP and incubated for another 20 min. The DNAs were then purified and analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis (c). Intensities of catenated and knotted DNAs were quantified. In each experiment, values of the topo IIα-ΔCTD reaction were normalized to those of the topo IIα-FL reaction. The mean ± s.d. from three independent experiments is shown (d). e Chromatid reconstitution assays were performed with topo IIα-FL or topo IIα-ΔCTD in a buffer containing 80 mM KCl. After a 150-min incubation at 22 °C, the mixtures were diluted by adding the same volume of reaction mixtures containing 80 mM KCl or 220 mM KCl so that the final concentrations of KCl became 80 mM or 150 mM. After another 20-min incubation at 22 °C, the resultant chromosomes were fixed and processed for immunolabeling. Blow-up images of cropped parts (indicated by the dashed rectangles in the merged images) are shown in grayscale. This experiment was repeated three times with similar results. Bar, 5 µm.