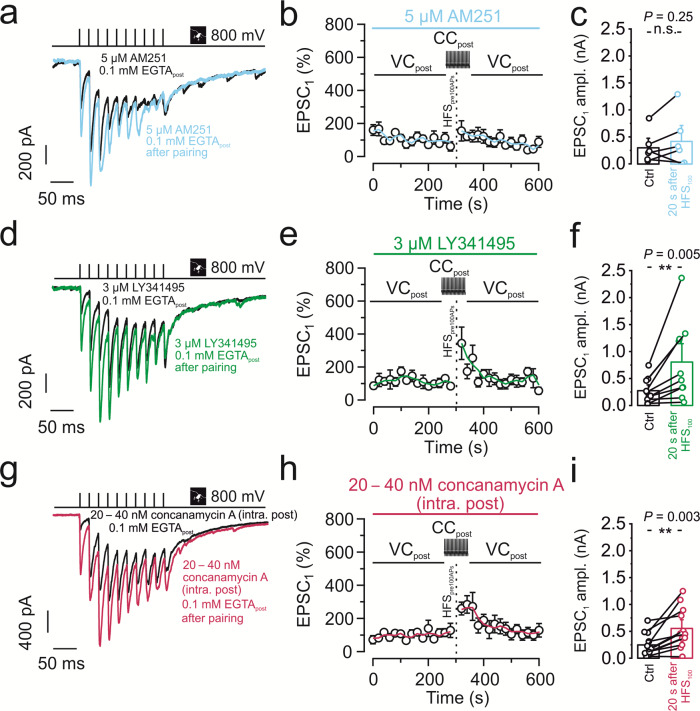
Fig. 4. Anti-associative PTP involves retrograde glutamate signaling and activation of presynaptic mGluR2/3 receptors.
a–c 5 µM of the CB1 receptor antagonist / inverse agonist AM251 did not restore PTP after pairing 100 presynaptic APs with postsynaptic APs with 0.1 mM EGTA in the postsynaptic pipette. a Representative traces of control (black) and after PTP induction (light blue). b Normalized EPSC1 amplitude plotted versus experimental time. Black vertical dashed line indicates PTP induction, pairing HFS100 stimulation (1 s, 100 Hz) in the presynaptic terminal (tight-seal cell-attached mode) with spiking in the postsynaptic neuron (whole-cell current-clamp configuration). Light blue line shows running average. Light blue horizontal bar on top indicates the application period of the CB1 receptor antagonist / inverse agonist. c Summary bar graph showing the EPSC1 amplitude before (“Ctrl”; black) and after pairing 100 presynaptic APs with postsynaptic APs (“20 s after HFS100”; light blue) in the presence of 5 µM AM251. d–f 3 µM of the mGluR2 / mGluR3 antagonist LY341495 largely restored PTP after pairing 100 presynaptic APs with postsynaptic APs with 0.1 mM EGTA in the postsynaptic pipette. d Representative traces of control (black) and after PTP induction (green). e Normalized EPSC1 amplitude plotted versus experimental time. Black vertical dashed line indicates PTP induction, pairing HFS100 stimulation (1 s, 100 Hz) in the presynaptic terminal (tight-seal cell-attached mode) with spiking in the postsynaptic neuron (whole-cell current-clamp configuration). Green line shows running average. Green horizontal bar on top indicates the application period of the mGluR2/3 receptor antagonist. f Summary bar graph showing the EPSC1 amplitude before (“Ctrl”; black) and after pairing 100 presynaptic APs with postsynaptic APs (“20 s after HFS100”; green) in the presence of 3 µM LY341495. g–i 20–40 nM of the H+-ATPase inhibitor concanamycin A (also called folimycin) in the postsynaptic pipette largely restored PTP after pairing 100 presynaptic APs with postsynaptic APs. g Representative traces of control (black) and after PTP induction (magenta). h Normalized EPSC1 amplitude plotted versus experimental time. Black vertical dashed line indicates PTP induction, pairing HFS100 stimulation (1 s, 100 Hz) in the presynaptic terminal (tight-seal cell-attached mode) with spiking in the postsynaptic neuron (whole-cell current-clamp configuration). Magenta line shows running average. Magenta horizontal bar on top indicates the application period of the H+-ATPase inhibitor. Note that the time course of PTP in the presence of concanamycin A is slightly different from that of control data sets, suggesting that a remaining suppression is more short-lasting. i Summary bar graph showing the EPSC1 amplitude before (“Ctrl”; black) and after pairing 100 presynaptic APs with postsynaptic APs (“20 s after HFS100”; magenta) in the presence of 20–40 nM of concanamycin A. c, f, i Boxes represent mean values, and circles show individual measurements. A paired non-parametric two-sided Wilcoxon signed rank test was used to test for statistical significance. ** indicates P < 0.01, and n.s. denotes non-significant difference (P ≥ 0.05). Data in (b, c), (e, f), and (h, i) are from 6, 10, and 12 pairs, respectively. Error bars indicate SEM.