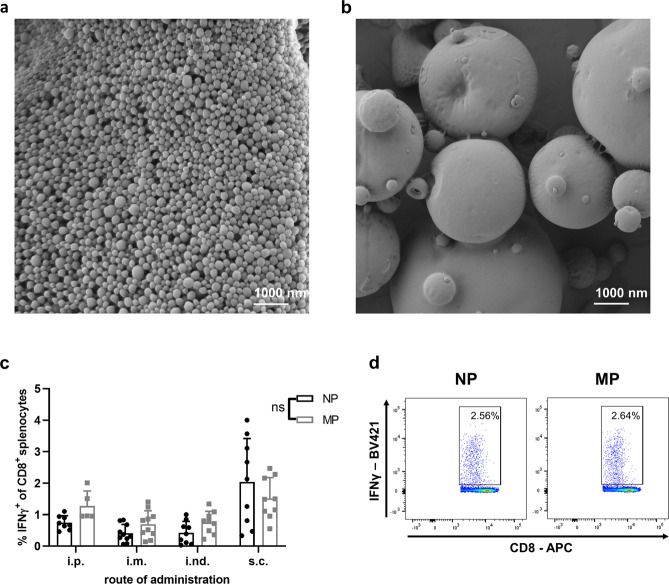
Fig. 1. Nano- or micron-sized PLGA particles containing ovalbumin (OVA) and Riboxxim are potent vaccine delivery systems for vaccination.
a, b Size distribution and morphology of nanoparticles (a) and microparticles (b) containing encapsulated OVA and Riboxxim were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Scale bars, 1000 nm. SEM images were acquired from three different particle batches with similar results. c C57BL/6J mice were immunized with nanoparticles (NP, black dots) or microparticles (MP, gray squares) charged with OVA protein (250 µg/mouse) and Riboxxim (2.5 µg/mouse) via the intraperitoneal (i.p., n = 8 for NP, n = 5 for MP), intramuscular (i.m., n = 10 for NP, n = 10 for MP), intranodal (i.nd., n = 9 for NP, n = 9 for MP), or subcutaneous (s.c., n = 9 for NP, n = 9 for MP) route demonstrating the latter as most efficient. Six days post-immunization, an intracellular cytokine staining for IFNγ+ of CD8+ splenocytes was performed and analyzed via flow cytometry. Statistics: two-way ANOVA followed by Šídák’s multiple comparisons test with ns, not significant. Data are presented as means ± SD and represent pooled data from three independent experiments. d A representative dot plot showing the frequency of IFNγ+CD8+ splenocytes for indicated treatment groups.