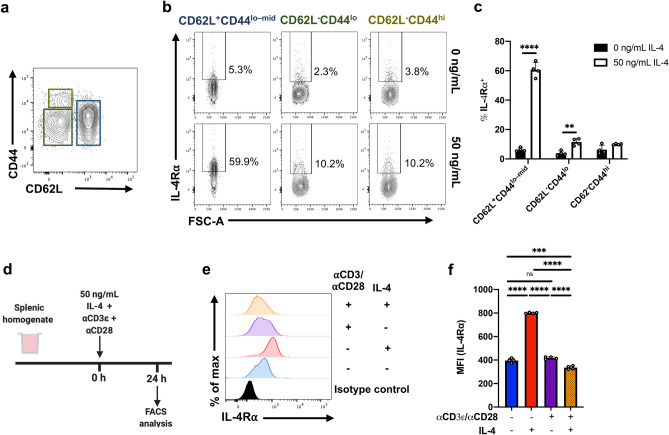
Figure 2.
IL-4R⍺ regulation is dependent on CD4 T cell CD62L:CD44 status. (a) Whole spleen homogenate derived from naïve 6–8-week-old female BALB/c mice (n = 4) were stimulated with 50 ng/mL IL-4 in vitro for 24 h prior to flow cytometric analysis. CD4 T cells were partitioned based on their CD62L:CD44 statuses. (b) Representative contour plots show the expression of IL-4R⍺ among CD4 T cells, with respect to CD62L and CD44. (c) The percentage of cells deemed IL-4R⍺+ following IL-4. (d) Splenic homogenate was seeded with ⍺CD3ε and ⍺CD28 and stimulated with 50 ng/mL of IL-4 for 24 h. (e) Representative histograms showing the expression profile of IL-4R⍺ on CD4 T cells and (f) MFI (IL-4R⍺) for each treatment condition was evaluated. Experiments were repeated three times. Two-way ANOVA combined with Tukey’s post-hoc multiple comparison test was conducted to compare groups. p-value denotations: ‘ns’ p ≥ 0.05, ‘*’p < 0.05, ‘**’p < 0.01, ‘***’p < 0.001 and ‘****’p < 0.0001.