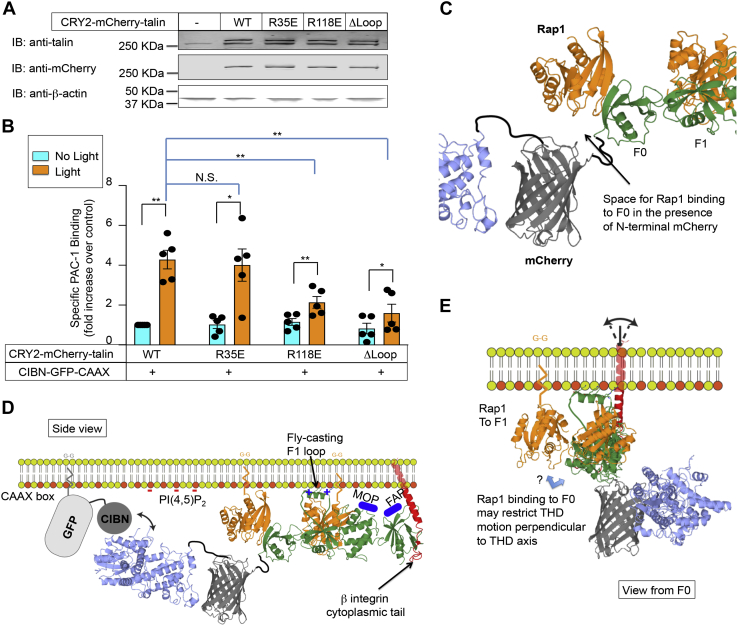
Figure 4.
αIIbβ3 activation requires direct interaction between talin and Rap1 after optogenetic recruitment of talin to the plasma membrane.A, talin mutations R35E, R118E, or ΔLoop were introduced into CRY2–mCherry–talin and the latter stably expressed along with C1BN–GFP–CAAX in A5 cells. Expression of CRY2–mCherry–talin was examined using anti-talin and anti-mCherry antibodies. β-Actin was monitored as a loading control. B, cells were treated with or without blue light and αIIbβ3 activation was assessed by specific PAC-1 binding. Data represent the means ± SEM of five experiments (double asterisk, p < 0.01; asterisk, p < 0.05). C, model of the CRY2–mCherry–talin head domain (THD) F0/F1 region. Note that two binding sites for Rap1–GTP (shown in orange) are potentially available within F0 and F1 subdomains of CRY2–mCherry–talin. D, view of CRY2–mCherry–THD as seen from the angle of the plasma membrane where CRY2 binds to CIBN–GFP–CAAX. This model summarizes the interactions of THD at the plasma membrane. Negatively charged PtdIns(4,5)P2 is shown as red dots; two Rap1 molecules are depicted in orange; the integrin β-tail traversing the plasma membrane is depicted in red. The structure of CIBN is not available, so it is drawn to scale according to its molecular weight. Both Rap1–GTP and CIBN–GFP–CAAX are membrane-associated via their C-terminal geranyl–geranyl (G–G) moieties. Upon contact with Rap1 and negatively charged phospholipids, the F1 loop in the THD is modeled to switch into the helical state, resulting in a cluster of positive charges to interact with plasma membrane. In addition, F2–F3 subdomains contain regions that face the membrane and interact with negatively charged phospholipids. They include the F2 membrane orientation patch (MOP) and the F3 association patch (FAP) (both shown in blue). E, view of CRY2–mCherry–THD as seen from the angle of the F0 subdomain on the plasma membrane. Note that the position of Rap1 bound to the F1 subdomain is perpendicular to the THD axis. CRY2, Arabidopsis cryptochrome 2; N.S., not statistically significant; PAC-1, activation-dependent anti-αIIbβ3 monoclonal antibody; PtdIns(4,5)P2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; Rap1, Ras-related protein 1.