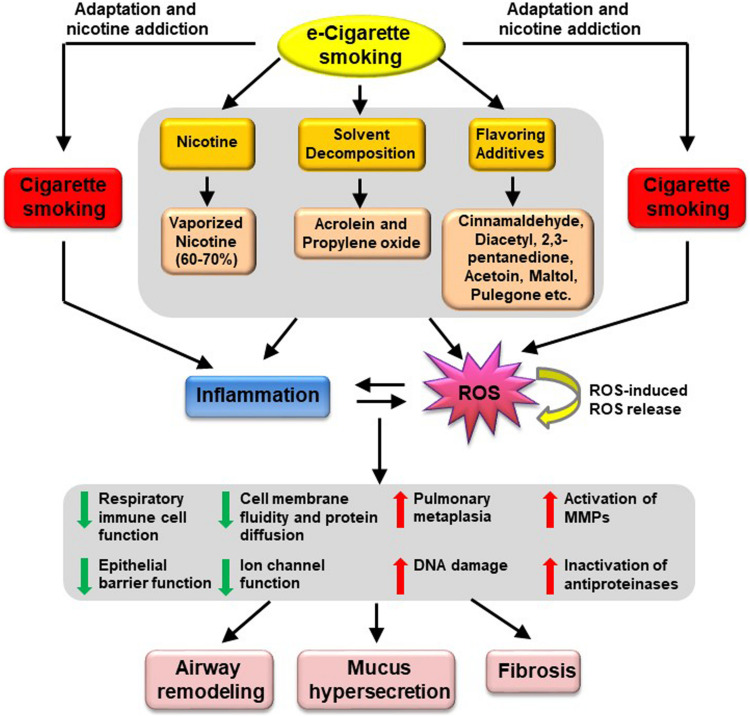
FIGURE 1.
Proposed mechanisms underlying e-Cigarette-induced pathogenesis of COPD. Vaping of e-Cigarettes produces vaporized nicotine and solvent decomposition products (i.e., acrolein and propylene oxide); together with flavoring additives such as cinnamaldehyde, diacetyl, 2,3-pentanedione, acetoin, maltol, pulegone, these products are known to induce oxidative stress and inflammation, which will in turn trigger cellular responses including reduced respiratory immune cell function, impaired epithelial barrier function, reduced cell membrane fluidity and protein diffusion, reduced ion channel function, increased pulmonary metaplasia, increased DNA damage, increased activation of MMPs and increased inactivation of antiproteinases. These pathophysiological alterations may ultimately lead to airway remodeling, mucus hypersecretion, and fibrosis, resulting in development of COPD. MMPs, metalloproteinases.